release time:2023-09-14 09:32:19
Semi-automatic biochemical analyzers are essential tools in healthcare settings, offering stable performance, affordability, and ease of use. They are particularly valuable in urban community outpatient departments and rural health centers, where qualified testing professionals are often scarce. However, to ensure the accuracy of biochemical test results and avoid potential medical disputes, it is crucial to implement quality control measures throughout the testing process. Here are five key ways to improve the accuracy of semi-automatic biochemical analyzers:
Semi-automatic biochemical analyzers are the linchpin of the testing system, demanding flawless performance. Environmental factors such as voltage, temperature, and humidity can affect their stability, so it's imperative to eliminate these interferences. Before each use, stringent calibration procedures should be followed.
Ensure compatibility between the analyzer and reagents, calibrators, and quality control products. Adhere to the operating procedures meticulously to achieve reliable test results. Even when using open reagents, opt for qualified ones and conduct multiple calibrations to prevent systematic errors.
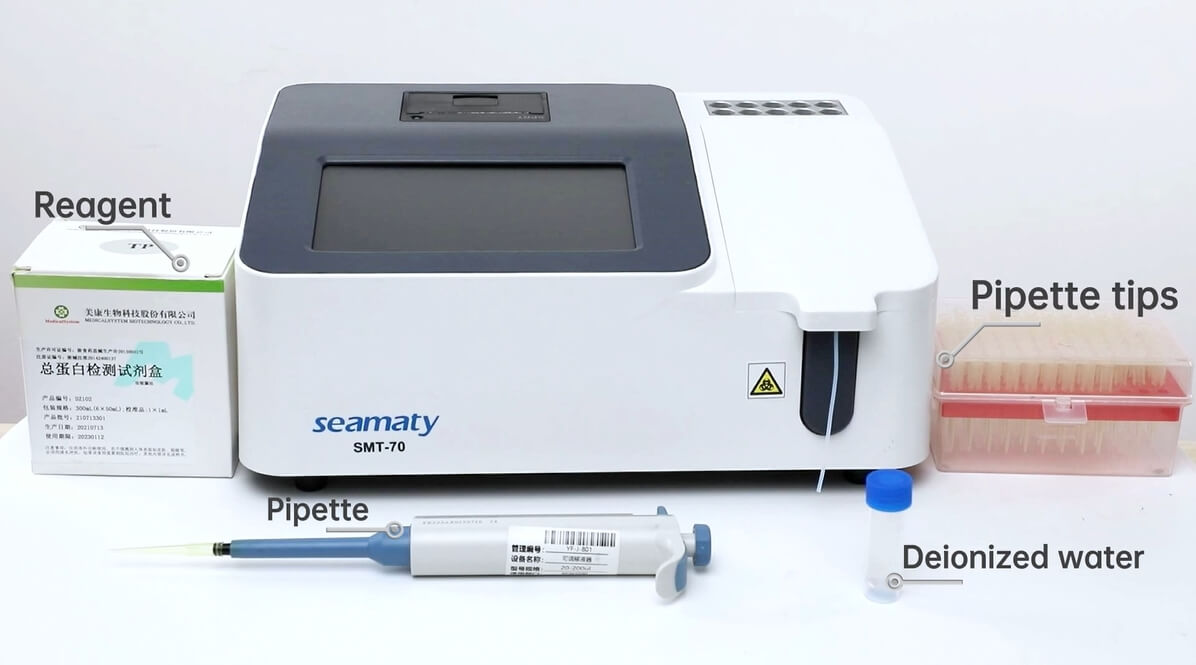

The accuracy of test results heavily depends on the quality of the blood samples collected. If a specimen doesn't meet the necessary quality requirements, it's best to refrain from testing it. Conditions like hemolysis, jaundice, celiac blood, and the presence of anticoagulants can significantly impact electrolyte levels, such as potassium, sodium, chloride, lactate dehydrogenase, and HDL cholesterol. For subpar blood samples, centrifugation and dilution should be employed to ensure compliance with testing standards.

Manual spiking in semi-automated biochemical analysis requires precision, especially when dealing with microliter-sized specimens like serum or plasma. Accuracy in spiking is crucial, as even slight variations can lead to vastly different results. Avoid mixing rate method (KIN) and two-point method (TP) determinations in advance. Instead, mix the specimen and reagents immediately before intake into the analyzer. This allows you to monitor absorbance changes during the reaction, ensuring accurate results.
Calibration is pivotal in the biochemical testing process, serving as a reference standard for the entire system. During the initial setup of the semi-automatic biochemical analyzer, calibration is performed for test items and adjustments related to reagents and experimental parameters. The key is to ensure that the calibration solution (calibrator) has a clear traceability, accurate assignment, and identification. Any discrepancies between the actual concentration and the labeled concentration can result in serious errors. It's essential to understand that semi-automated biochemical analysis is primarily based on spectroscopic analysis, following the Lambert-Beer law. Therefore, fluctuations in the concentration of the calibration solution and sample alignment errors must be addressed by reducing the number of calibrations when reagents and experimental parameters are stable. Continuous indoor quality control should also be conducted to monitor precision and guarantee result accuracy.

Occasionally, high specimen concentrations may surpass the linear range of the semi-automatic biochemical analyzer or experimental method. In such cases, specimens must be diluted and retested, with the final result multiplied by the dilution factor. Additionally, UV (340nm) detection monochromators are susceptible to damage due to prolonged use, humidity, and high temperatures, potentially affecting the accuracy of biochemical test results. Regular maintenance and timely adjustments are essential to mitigate these issues.
|
Steps |
Description |
|
1. Thorough Calibration of Instruments and Reagents |
Ensure the analyzer's reliable performance by calibrating it meticulously to eliminate environmental interferences. Use compatible reagents and follow strict operating procedures to prevent systematic errors. |
|
2. Precise Blood Sample Collection |
Collect high-quality blood samples that meet testing requirements. Address issues like hemolysis, jaundice, and anticoagulants. Employ centrifugation and dilution for unqualified samples. |
|
3. Careful Manual Spiking |
Achieve precision in manual spiking, especially with microliter-sized specimens. Avoid mixing determination methods in advance. Mix specimens and reagents immediately before testing for accurate results. |
|
4. Accurate Calibration |
Calibration is crucial; ensure calibration solutions have traceable and accurate concentrations. Beware of concentration changes due to evaporation or dilution during testing, which can lead to errors. |
|
5. Addressing High Specimen Concentrations and Equipment Maintenance |
For high specimen concentrations, dilute and retest, accounting for dilution factors. Maintain UV detection monochromators to prevent equipment-related inaccuracies. |
Semi-automatic biochemical analyzers require substantial manual involvement in the testing process. To enhance test quality, it's imperative to improve the proficiency of testing personnel. Strict adherence to standardized operating procedures, meticulous execution, and the assurance of reliable instrument performance, along with advanced experimental techniques, precise calibrations, and the use of qualified and effective reagents and consumables, are the keys to harnessing the full potential of semi-automatic biochemical analyzers for efficient and accurate testing.
- Recommended Further Reading
[1]. 6 Best Semi-Auto Biochemical Analyzers for Low-Budget Small Clinics
[2]. Fully Automatic Chemistry Analyzer vs. Semi-Auto Chemistry Analyzer: Which One Is Better?
[3]. Biochemical Testing: Semi-auto Biochemistry Analyser Vs Plate Reader
[4]. Maintenance of semi auto biochemistry analyzer | semi auto analyser
[5]. 8 tips for using semi-automatic biochemistry analyzer
[6]. Common Errors and Pitfalls in Clinical Chemistry Analyzer Testing

2025-02-27
Discover the Seamaty VG2 Blood Gas & Immunoassay Analyzer, an all-in-one veterinary diagnostic device delivering fast and accurate results in just 10 minutes. Ideal for emergency care, anesthesia monitoring, and chronic disease management, it optimizes workflow, reduces costs, and enhances veterinary clinic efficiency.

2024-02-18
Explore the intricacies of CLIA Analyzers in this comprehensive guide. Uncover their significance in medicine, understand the working principles with simplified explanations, and discover various types, including the advanced Seamaty SMT780.
2022-02-18
A biochemistry test is a biochemistry analyzer that measures the levels of enzymes, proteins, lipids and other metabolites in the blood to determine the function of various systems and organs.