release time:2024-04-09 16:24:58
In vitro diagnostic (IVD) reagents are the silent workhorses of modern medicine. These essential tools play a critical role in medical research and clinical testing by providing:
With the ever-expanding world of IVD reagents, understanding their different types and the science behind them can seem complex. But fear not! This blog post will serve as your guide, demystifying IVD reagents by exploring the three key categories and diving into nine essential technical principles.

IVD reagents can be classified into three main categories based on their area of application in clinical practice:
1. Clinical Specialty:
2. Methodology:
This category focuses on the specific technique used in the IVD reagent. Here are some common methods: * Chemical colorimetric method: Measures the color intensity of a solution to determine the concentration of a substance. * Immunoturbidimetric method: Detects antigen-antibody reactions by measuring the turbidity (cloudiness) of a solution. * Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA): Uses enzymes to detect and quantify antigens or antibodies.
3. Other methodologies include immunofluorescence, chemiluminescence, and various techniques used in molecular biology.
Now that we've explored the different categories, let's delve into nine key technical principles that make IVD reagents function:
1. Spectral Analysis Techniques: These methods analyze the interaction between light and matter. They encompass atomic spectroscopy (analyzing elements) and spectrophotometry (measuring light absorption).
2. Electrochemical Analysis Methods: These techniques measure a substance's electrical properties. Examples include measuring electric potential, electrical resistance, and changes during titration.
3. Immunodiagnostic Techniques: These methods exploit the specific interaction between antigens and antibodies. ELISA and immunoturbidimetry are prime examples.
4. Immunofluorescence Technique: This technique uses fluorescent molecules attached to antibodies to visualize antigens under a microscope.
5. Flow Cytometry: This advanced method allows for the rapid analysis and sorting of individual cells based on their surface and internal properties.
6. Colloidal Gold Technology: This technique utilizes gold nanoparticles to detect the presence of target molecules in a sample.
7. Chemiluminescence Immunoassay: This method harnesses the emission of light during a chemical reaction to detect antigens or antibodies.
8. Nucleic Acid Molecular Hybridization Technology: This technique identifies specific DNA or RNA sequences by their ability to bind complementary strands.
9. DNA Sequencing Technology: This powerful tool determines the exact order of nucleotides (building blocks) in a DNA molecule.
The three key categories and nine technical principles we've explored represent just a glimpse into the fascinating world of IVD reagents. These versatile tools are constantly evolving, pushing the boundaries of medical diagnostics and enabling better patient care. By understanding the fundamental principles behind them, we can appreciate the remarkable power of IVD reagents in safeguarding our health.
2025-03-14
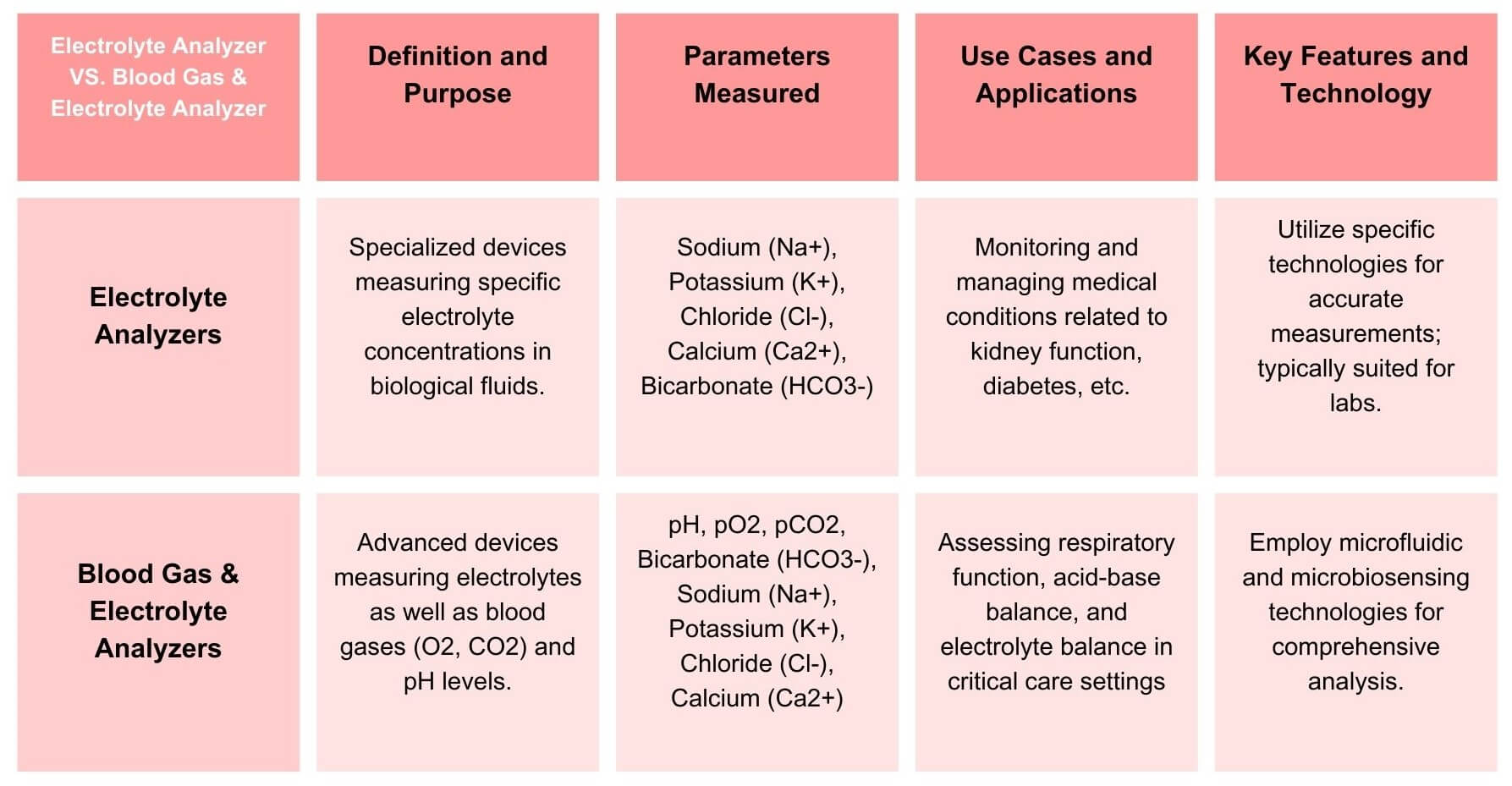
Explore the differences between Electrolyte Analyzers and Blood Gas & Electrolyte Analyzers. Learn their functions, advantages, and applications for informed healthcare choices. A comprehensive comparison for medical professionals and enthusiasts.

2023-11-15
Explore the latest advancements in medical technology with our comprehensive guide to the top 8 blood gas and electrolyte analyzers in 2024. From handheld devices for on-the-go diagnostics to benchtop systems offering diverse testing parameters, discover the key features, testing times, and average prices of these cutting-edge analyzers. Stay informed for smarter healthcare decisions.

2022-09-21
Seamaty is one of the top medical equipment suppliers in China, specializing in the development, manufacture and sales of in vitro diagnostic equipment and reagents. Its product range includes biochemistry, coagulation, immunology, blood gas and electrolytes, PCR and animal ultrasound.