release time:2021-09-07 11:53:07
Semi auto analyser means that some of the operations in the analysis process (such as adding samples, holding, inhalation colorimetry, result recording and other certain steps) need to be done manually. The semi auto analyser is characterized by its small size, simple structure and flexibility, and can be used separately. At the same time, semi-automatic biochemical analyzers can be used in conjunction with other medical equipment. Most importantly, semi-automatic biochemistry analyzers are very inexpensive.
The fully automated biochemistry analyzer is fully automated from sample addition to result generation. The operator only needs to put the sample on the specific position of the analyzer and choose the program to start the instrument to take the test report.

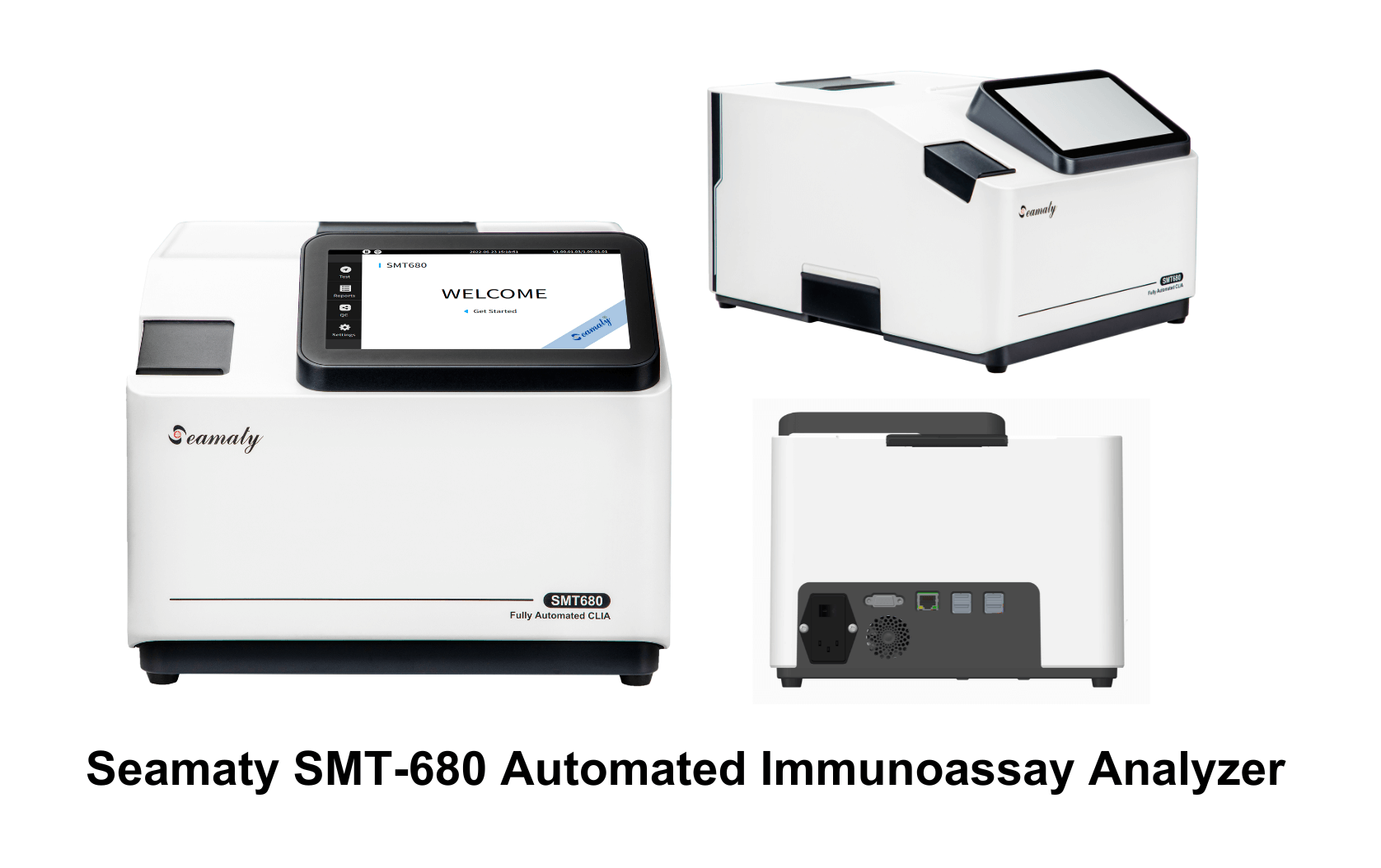
2023-05-05
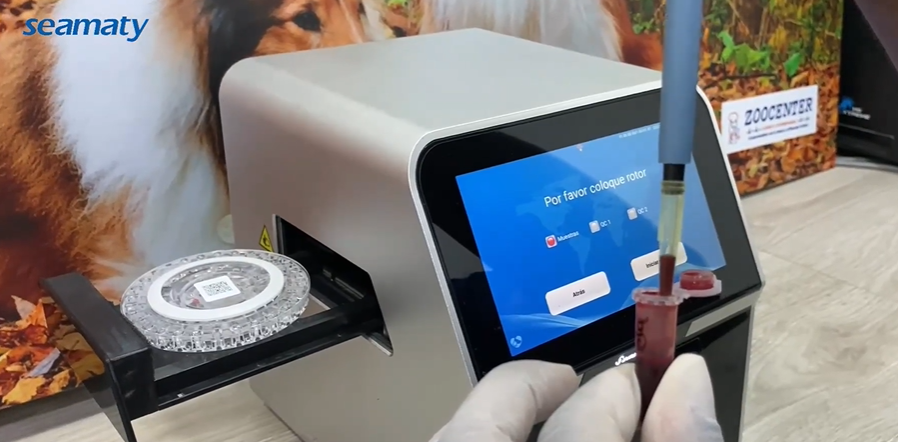
Maximize the value of your Seamaty automated immunoassay analyzer with our tips and best practices. Learn about regular maintenance, proper handling of reagents, optimizing assay parameters, appropriate operator training, quality control measures, and troubleshooting common issues. Follow these guidelines to ensure accurate and reliable results.

2022-08-22
A wide variety of POC devices are available for point-of-care diagnostics. A few common POC devices are listed below.
2021-11-10
Speaking of biochemical testing, for enzyme student chemistry testing, electrolytes and other hemolysis, lipidemia, jaundice samples are of great impact. Therefore, in the use of fully automated biochemical analyzers, the pre-treatment of blood samples is essential both from the test results and testing efficiency.