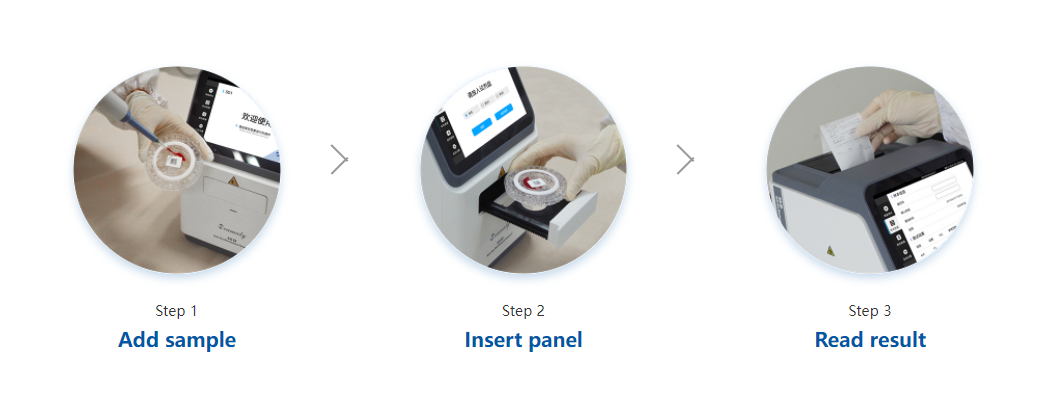
A dry chemistry analyzer is a device used to analyze samples without the use of liquids. This type of analyzer is often used in medical and scientific settings, as it can provide accurate results without the need for expensive or delicate liquid reagents. Dry chemistry analyzers typically work by using heat, light, or electricity to induce chemical reactions in the sample being analyzed. These reactions are then monitored and recorded, allowing the analyzer to generate accurate results. While dry chemistry analyzers are not suitable for all types of analysis, they can be an invaluable tool in many settings.
Dry chemistry analyzers are Point of Care Testing (POCT) devices used to measure various components in a blood sample. The most common use for these analyzers is to measure blood sugar levels, but they can also be used to test for other parameters such as hemoglobin levels and potassium levels. While there are a number of different dry chemistry analyzers on the market, all work by measuring the light absorbance or fluorescence of colored dyes in a blood sample. This article will provide an overview of how dry chemistry analyzers work, as well as the pros and cons of using them in a clinical setting.

1. What is a POCT device and what are its benefits?
A
point-of-care testing (POCT) device is a medical diagnostic tool that is used to perform tests on patients at the point of care, which is generally defined as being at or near the site of the patient's care. POCT devices are usually portable and easy to use, and they offer a number of benefits over traditional laboratory testing methods. Perhaps the most significant advantage of POCT is that it can provide rapid results, which can be critical in emergency situations. Another benefit is that POCT can be performed without the need for trained laboratory personnel, which can make it more convenient and cost-effective. In addition, POCT devices often require smaller amounts of blood or other specimens than traditional laboratory tests, making them less invasive for patients. While there are some limitations to point-of-care testing, such as its lower accuracy compared to laboratory tests, its advantages make it an important tool in a variety of settings.
2. How does a dry chemistry analyzer work?
The analyzer typically consists of three main components: a sample chamber, a reagent chamber, and a reaction chamber. The sample chamber is where the bodily fluid is placed. The reagent chamber contains the dry chemicals that will react with the sample. And the reaction chamber is where the actual chemical reaction takes place. To use the analyzer, a small amount of the bodily fluid is placed in the sample chamber and then drawn into the reagent chamber. The dry chemicals in the reagent chamber react with the sample, producing a color change that can be measured quantitatively. The amount of color change is then used to calculate the concentration of the analyte in the sample. Dry chemistry analyzers are simple to use and require little to no maintenance, making them well suited for point-of-care applications.
3. The different types of tests that can be performed with a dry chemistry analyzer
Point of care testing devices has become increasingly popular in recent years, as they offer a quick and convenient way to perform a variety of tests. One type of point of care testing device is a dry chemistry analyzer. Dry chemistry analyzers can be used to perform a variety of tests, including blood tests, urine tests, and fecal tests. Blood tests can be used to measure things like hemoglobin levels, hematocrit levels, and blood glucose levels. Urine tests can be used to measure things like urinary tract infections, kidney function, and pregnancy. Fecal tests can be used to measure things like gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammatory bowel disease, and parasite infections. Dry chemistry analyzers are an essential tool for point of care testing, and they can provide valuable information about a patient's health.
4. The advantages of using a POCT device in a clinical setting
Point-of-care testing (POCT) devices are becoming increasingly popular in clinical settings for a number of reasons. First, they offer a quick and convenient way to obtain test results. Second, they can be used by personnel with varying levels of training, which can help to reduce costs. Third, they are typically easy to use and require minimal maintenance. Finally, point-of-care testing devices can be a valuable tool for monitoring patients with chronic conditions or those who are at risk for complications. In general, point-of-care testing devices can help to improve patient care by providing timely and accurate information.
5. How to choose the right POCT device for your needs
Point of care testing devices is medical devices that are used to test for various conditions and diseases. There are many different types of point of care testing devices, and it is important to choose the right one for your needs. One type of point of care testing device is a dry chemistry analyzer. Dry chemistry analyzers use a chemical reaction to test for various conditions and diseases. Another type of point of care testing device is an immunoassay analyzer. Immunoassay analyzers use antibodies to test for various conditions and diseases. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine which type of point of care testing device is right for you.
Conclusion
The benefits of using POCT devices in a clinical setting are clear. They allow for fast, accurate, and convenient testing that can help improve patient care. When choosing a POCT device, it is important to consider the needs of your clinic and the types of tests you will be performing. With the right device, you can ensure that your patients receive the best possible care.