release time:2021-11-08 16:41:25
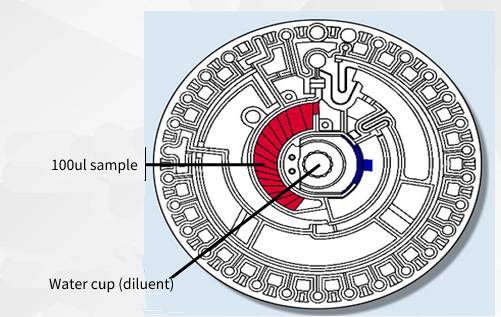
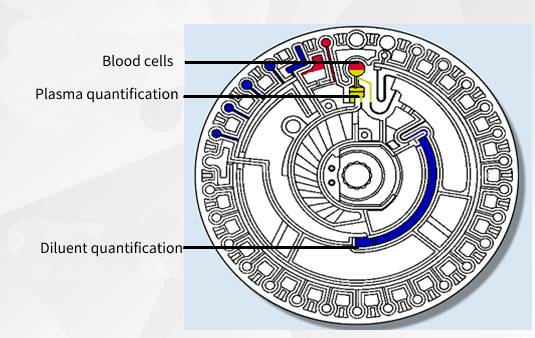
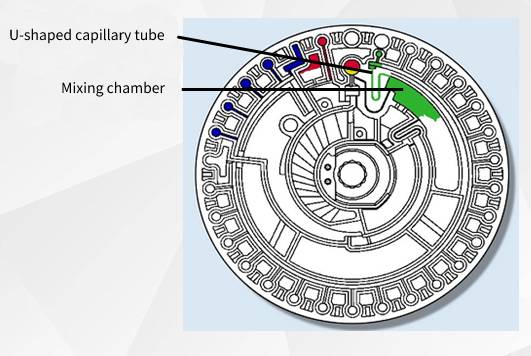
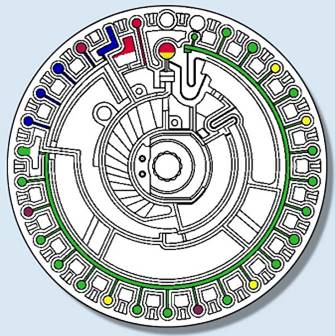
The built-in motor of the biochemical instrument drives the test disc at high speed. Under centrifugal force, the sample and diluent move towards the outer periphery away from the center of the test disc (built-in centrifugation). After a period of high-speed operation, the sample is separated into plasma against the center of the circle, a fixed volume, and blood cells against the periphery by a small centrifugal force (sample centrifugation for quantitative stratification). On the other hand, a certain volume of diluent is retained in the circular cavity. The rest enters the quality control chamber for comparable color assays and the excess diluent collection chamber.

2022-06-22
These blood analyzers are very useful in providing quick and accurate information about the blood cell count and its properties. The most common information obtained with the help f these analyzers are

2022-05-17
A simple formula to describe POCT devices is "Point-of-care diagnostic products = fast + accurate + small instruments". most point of care testing devices have undergone a process of gradual simplification and improvement from traditional testing methods to achieve convenient and rapid on-site examination at the patient's side for the purpose of rapid diagnosis.
2022-02-23
Blood biochemistry is an important part of clinical biochemistry testing. With the rapid development of science and technology, more and more scientific research results are applied to blood biochemistry tests,