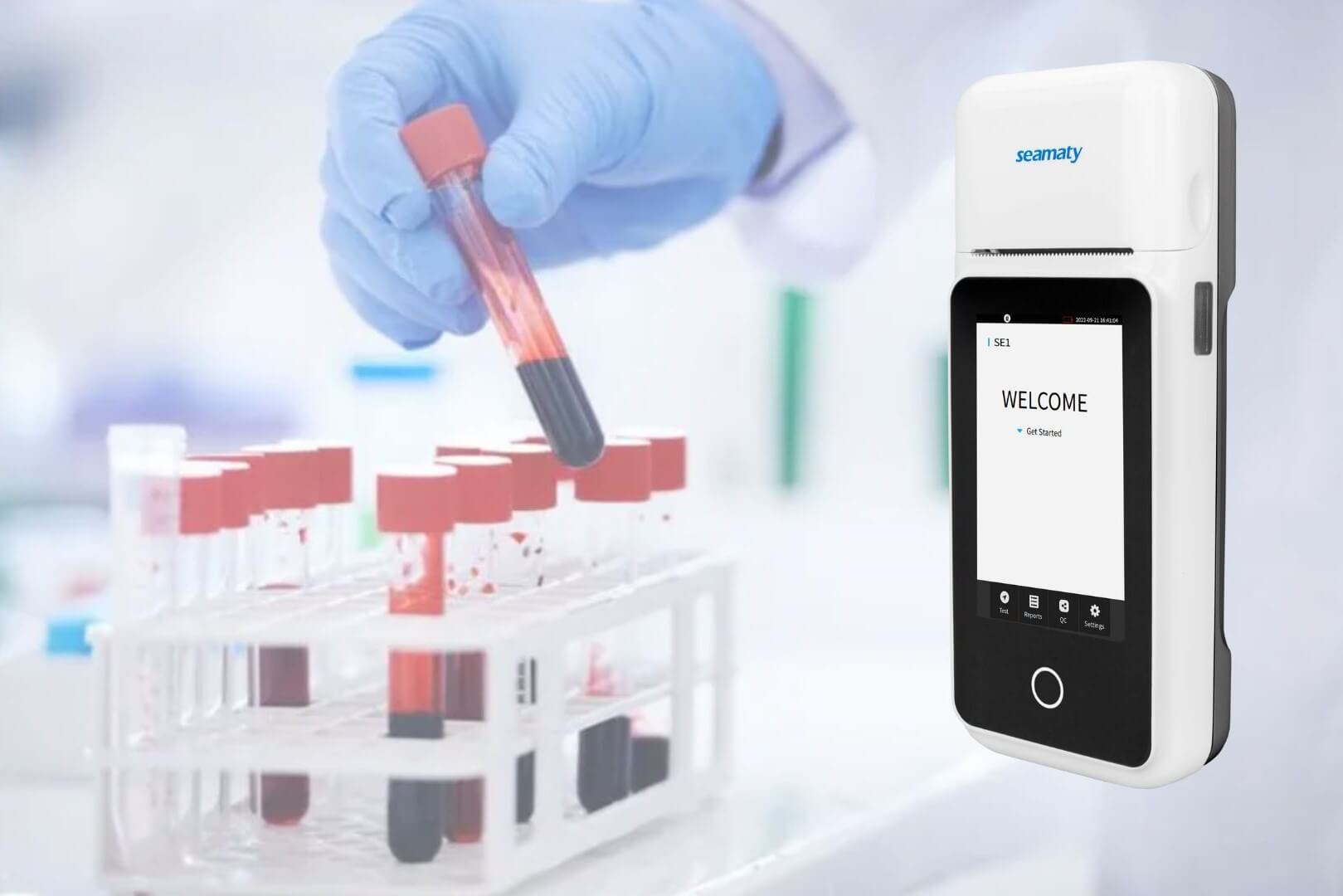
As the standard of living improves, the number of dogs and cats with obesity and advanced age is increasing. Diabetes has also become the number one chronic disease plaguing pets. Some data show that about 1 in 100 dogs have the worry of diabetes. And the worrying thing is: this number is still on the rise.
01 What is diabetes mellitus?
Cause: A metabolic disease in which the level of glucose in the blood is abnormally elevated due to insufficient insulin secretion or impaired insulin bioavailability in the body.
02 Clinical characteristics of diabetes mellitus in animals
-
a. Chronic disease.
-
b. Usually presents with elevated blood glucose as the basic feature.
-
c. The disease is often combined with polydipsia and polyuria, hyperlipidemia and fatty liver at the beginning of the disease. The disease gradually worsens over time and manifests itself as a metabolic syndrome with multi-organ lesions and infections.
The three forms of diabetes mellitus according to clinical manifestations
-
-Typical diabetic symptoms
-
-Diabetic ketoacidemia
-
-Peripheral neuropathy
03 Keys to diabetes mellitus
Proper insulin therapy and dietary management
04 Monitoring of diabetic animals
-
- Clinical signs
-
- BGCS
-
- Laboratory monitoring indicators (LAC, FRUC, ALT, AST, urinalysis...)
05 Clinical manifestations
-
-Polydrinking
-
-Polyuria
-
-Increased appetite
-
-Weight loss, wasting
-
-Cataracts
-
-Increased abdominal girth
-
-Wounds that do not heal
-
-Abnormal gait...
06 BGCS (blood glucose profile)
-
-Can't pursue a standard blood glucose curve
-
-Monitoring multiple bars
-
-Used to guide and evaluate insulin therapy
-
-Better to make a blood glucose curve at home than in the hospital
-
-Details of interest: blood glucose minimum, duration of action, whether the curve is smooth
07 Laboratory monitoring indicators
-
-Fructosamine (FRUC): monitoring reflects the blood glucose level of the animal over a period of 1-2 weeks.
-
-Lactic acid (LAC): an intermediate product of the body's sugar metabolism. It can be used as a more sensitive and reliable indicator of tissue hypoxia.
-
-Amylase (AMY), lipase (LPS)
-
-Liver enzymes (including aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase)
08 Summary
-
● Raise the awareness of owners on animal medical examination
-
●Good "education" for owners: regular review at the hospital (including electrolytes, liver and kidney function, fructosamine, urine ketone body testing)
-
●Diagnosis of diabetes requires caution
09 Seamaty test reagents: 9 items of diabetes, 9 items of blood gas electrolytes
Diabetes testing reagent features
Fructosamine can more accurately diagnose diabetes that has occurred in animals within the last 1-2 weeks. It is also effective in ruling out hyperemia caused by stress (especially in cats). Fructosamine is also effective in responding to the effects of insulin therapy through continuous monitoring (once every 7 days).
Clinical cases presenting with polydipsia and polyuria and high blood glucose in biochemical tests can be diagnosed by fructosamine as being caused by diabetes and not by other renal urinary tract diseases. Also the triglycerides, cholesterol in this plate can be used for fat group of elderly cases. It can be used to detect the prevention of diseases such as high blood lipids and high blood sugar in the elderly.
Reagent disc test items: fructose gum (FRU), total cholesterol (TC), lactic acid (LAC), glucose (GLU), triglyceride (TG), lipase (LPS), amylase (AMY), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT)