release time:2025-03-06 10:22:10
To ensure that a biochemical analyzer meets clinical analysis standards, precision, accuracy, quality control, calibration, and standardization are crucial aspects for evaluating its performance. But what exactly do these five key performance indicators mean, and how are they interconnected? This article will provide you with a clear explanation all at once.
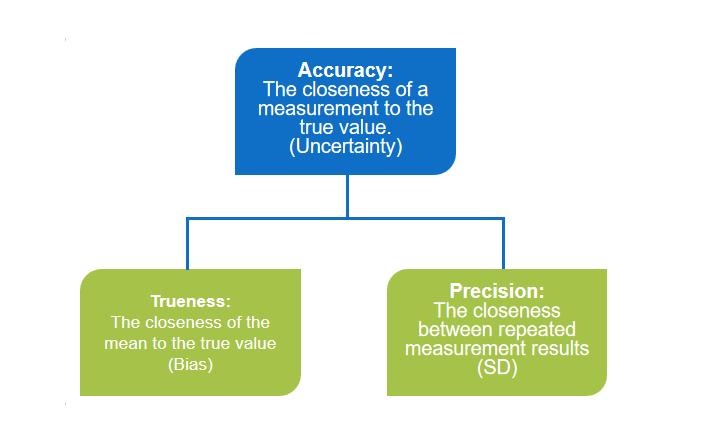
Trueness:
It refers to the closeness of the average measured value from multiple repeated measurements to the true value. Accuracy primarily reflects systematic measurement errors, indicated by bias, and is independent of random errors.
Precision:
It refers to the closeness of repeated measurements of the same sample under the same conditions.
Accuracy:
It indicates how well the measured values align with the true values, and accuracy is represented by the magnitude of the error.
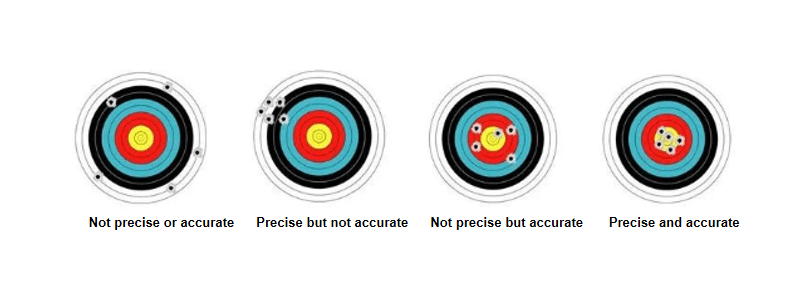
(1) High accuracy implies high precision.
(2) High precision does not necessarily mean high accuracy.
(3) Precision is a prerequisite for ensuring accuracy.
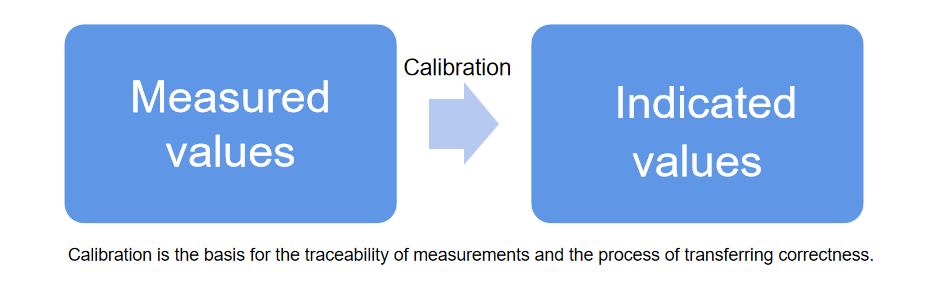
Calibration is used for quantitative detection, involving the calibration of test results for a specific detection item. A reference point (k value) is established, and a conversion curve is determined to transform absorbance values into concentrations or enzyme activities.
Quality control is divided into internal quality control (IQC) and external quality assessment (EQA).
Internal Quality Control (IQC):
Definition: IQC involves continuous evaluation of the reliability of laboratory work using specific methods and steps. Its aim is to monitor the precision of routine work within the laboratory and improve the consistency of within-batch and between-batch sample testing to determine the reliability of test results.
Process: Set the mean and QC rules for the detection system → daily QC sample testing → present results in the form of QC charts based on the mean and QC rules (including control measures) → maintain system stability.
External Quality Assessment (EQA):
Definition: EQA evaluates differences in analytical performance between peer group laboratories or between a laboratory and a reference laboratory. It assesses the accuracy of routine inter-laboratory evaluations and correctness evaluations to assess the accuracy of the testing method.
Process: Apply for participation in EQA program → multiple laboratories test the same EQA sample → the proficiency testing provider analyzes data and provides results (target values) → laboratories analyze the results and adjust the testing system to approach the target values step by step (converging results towards target values) → achieve system harmonization.

Quality control materials are stable substances used to inspect the performance of analytical instruments or methods, validating their performance.
1) Storage:
Store in a light-protected environment and place in a sealed box before refrigeration.
Quality control status
Storage conditions
Dry powder quality control product
2°C ~ 8°C
After re dissolution, pack and freeze storage
-10°C ~ -20°C
Liquid quality control product
-20°C ~ -70°C
2) Reconstitution:
a) Take a vial of quality control powder;
b) Add deionized water according to the instructions;
c) Open the bottle cap, inject sterile water along the groove;
d) Tighten the bottle cap, let it stand for 20 minutes, invert for 10 minutes, gently mix.
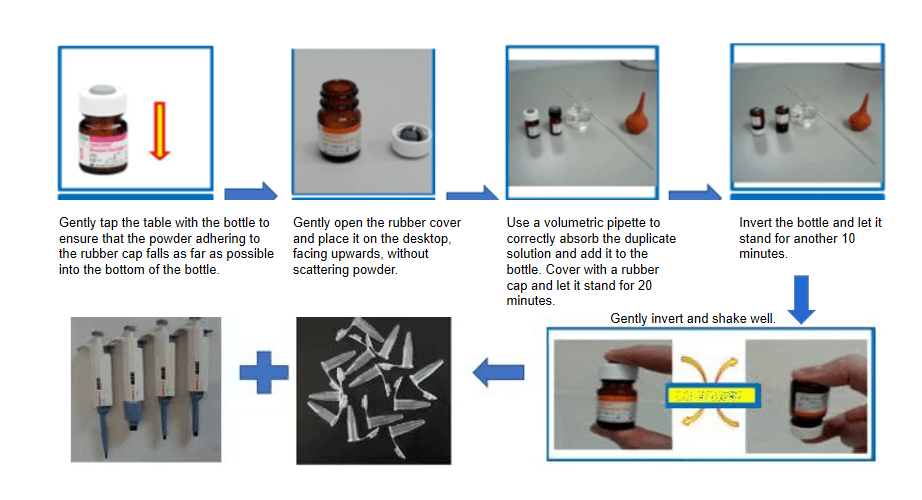

3) Comparison:
a) After testing, compare data results with target values;
b) If the error range is within 2 SD, it indicates accurate machine testing.
Calibration of the SD3 Biochemical Analyzer: No calibration required for customers
a) The instrument automatically performs self-check during startup, with error alarms for instrument malfunctions.
b) The instrument's optical energy automatically calibrates gain to avoid weakening of the light source affecting testing.
c) Each batch of reagent disks undergoes independent calibration before leaving the factory, with calibration information stored in the 2D code on the reagent disk, and the instrument automatically identifies and reads it before testing.
Quality Control of the SD3 Dry Biochemical Analyzer: It is recommended to use our recommended batch of quality control materials: UK Randox.
The Seamaty automatic biochemical analyzer adopts the analytical principle of large desktop biochemical analyzers and optical measurement technology. It also incorporates a real-time quality control system to ensure accurate testing.


2025-02-18
Discover the Seamaty SD3 Fully Automated Dry Biochemistry Analyzer, featuring microfluidic technology and a fan-shaped reagent disc for precise, 6-minute test results. Ideal for emergency care, primary clinics, and health check-ups, it offers fast, portable, and maintenance-free diagnostics.

2023-07-13
Become a successful distributor of affordable clinical chemistry analyzers. Learn from real cases and unleash your potential with expert insights and high-quality products.

2022-08-28
You are likely aware of the importance of blood testing for diagnosing and treating patients. One common type of blood test is a hematology analysis, which can help detect various diseases and conditions. A 3-part auto hematology analyzer is one type of machine that can be used for this purpose. Here's what you need to know about them.