release time:2025-03-04 10:49:15
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) refers to medical tests performed on human samples (such as blood, body fluids, and tissues) outside the body to obtain clinical diagnostic information. It plays a crucial role in disease detection, health monitoring, and treatment planning. IVD mainly includes molecular diagnostics, immunodiagnostics, and biochemical diagnostics. With advancements in technology, microfluidics has emerged as a key innovation in IVD, offering automation, rapid testing, ultra-high sensitivity, high-throughput detection, and minimally invasive procedures.
This article explores the application of microfluidics in IVD, focusing on three major areas: molecular diagnosis, immunodiagnosis, and biochemical diagnosis.

Molecular diagnosis detects genetic and protein-level changes in individuals or pathogens at the molecular level. It is widely used in infectious disease detection, genetic disorder screening, early cancer detection, prognosis assessment, precision medicine, and non-invasive prenatal testing. Among the various microfluidic applications, microfluidic polymerase chain reaction (PCR) chips have significantly enhanced molecular diagnostic capabilities.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a molecular biology technique used to amplify specific DNA fragments. It involves three key steps:
Denaturation (90°C - 95°C): DNA strands separate under high temperatures.
Annealing (55°C - 60°C): Primers bind to the target DNA sequences.
Extension (70°C - 72°C): DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands.
PCR plays a vital role in detecting infectious diseases, genetic mutations, and cancer biomarkers.
Microfluidic PCR chips integrate PCR technology with microfluidic systems to enable rapid, high-efficiency DNA amplification. These chips are characterized by:
Miniaturization: Reduces sample volume and reagent consumption.
High Speed: Faster temperature changes enhance reaction speed.
Automation & Integration: Reduces manual handling and risk of contamination.
Portability: Enables on-site or point-of-care testing (POCT).
There are different designs for microfluidic PCR chips:
Spatial Type: Fluid moves through different temperature zones in microchannels (e.g., snake form, radiating, closed-loop structures).
Temporal Type: Fluid remains stationary while the temperature changes (e.g., centrifugal chips).
LAMP (Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) Chips: Enable constant-temperature amplification without temperature cycling.
Digital PCR Chips: Distribute DNA into thousands of tiny partitions for absolute quantification based on fluorescence signals.
These advances have significantly improved molecular diagnostics, making them faster, more efficient, and more accessible.
Immunodiagnosis utilizes immunological principles to detect diseases and evaluate immune status. This method is widely applied in detecting infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer biomarkers.
Microfluidic immuno-chips have enabled highly sensitive, rapid, and automated immunodiagnostic tests. The key applications include:
Tumor Marker Detection: Measures specific cancer biomarkers for early diagnosis and monitoring treatment efficacy.
Infectious Disease Antigen/Antibody Detection: Identifies viral and bacterial infections through rapid antigen/antibody tests.
Autoimmune Disease Diagnosis: Detects autoantibodies, which are crucial for diagnosing conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
Hormone Testing: Measures hormone levels for endocrinological assessments.
Higher Sensitivity & Specificity: Detects minute amounts of antigens or antibodies with high precision.
Faster Results: Reduces turnaround time compared to traditional immunoassays.
Point-of-Care Testing: Enables rapid, on-site diagnosis for infectious diseases, improving patient management.
Lower Sample & Reagent Consumption: Reduces test costs while maintaining high accuracy.
These advancements make microfluidic immunodiagnosis essential for modern clinical and research applications.
Biochemical diagnosis involves analyzing body fluids (e.g., blood, urine) to assess metabolic functions and detect diseases. Common biochemical tests measure blood glucose, lipids, liver enzymes, kidney function markers, and cardiac enzymes. Biochemical analysis accounts for nearly 30% of the IVD market.
Traditional biochemical analysis relies on large, automated analyzers in medical institutions. While highly accurate, these systems have limitations:
Slow Processing: Sample-to-result time can be lengthy.
High Sample & Reagent Consumption: Requires larger volumes of blood and costly reagents.
Limited Accessibility: Not suitable for decentralized or point-of-care testing.
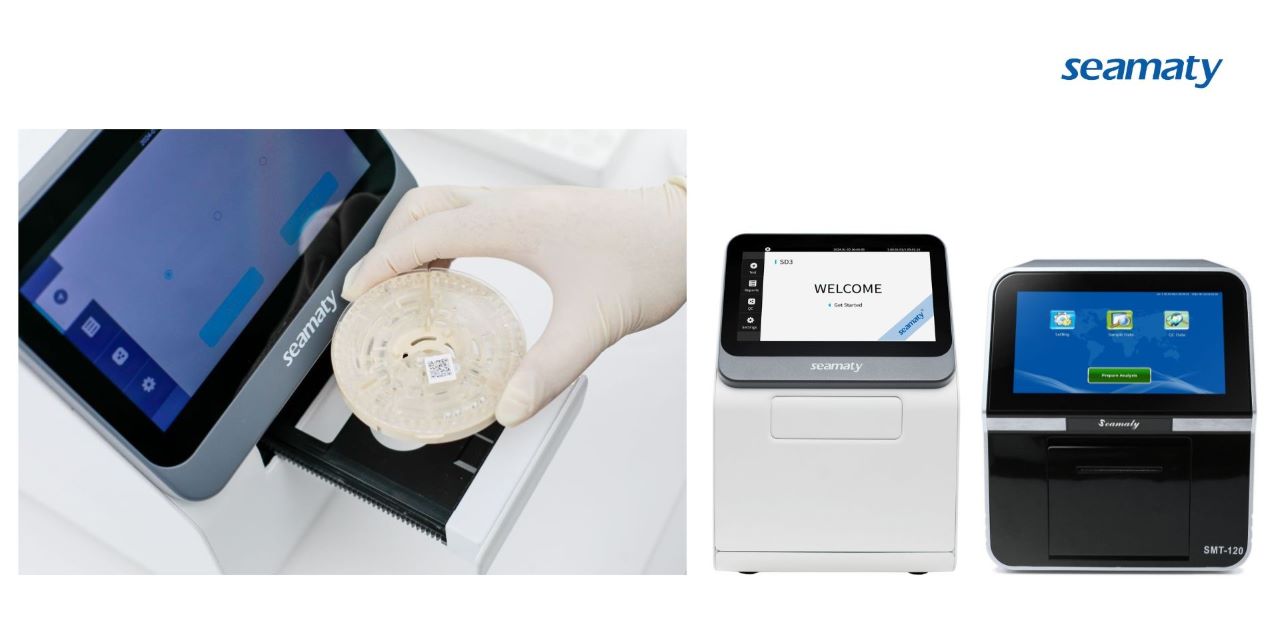

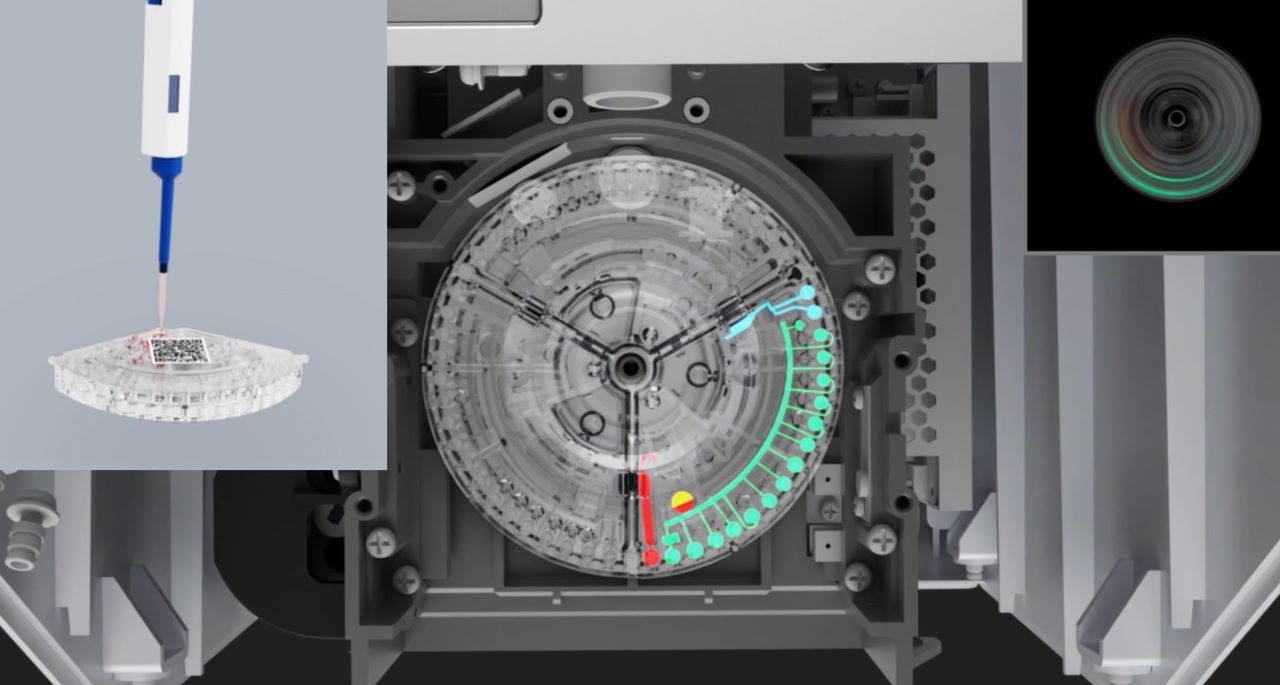
Microfluidic technology addresses these challenges by integrating multiple biochemical processes onto a single chip. Key benefits include:
Fully Integrated Automation: Microfluidic chips combine blood separation, quantification, dilution, and analysis in a compact system.
Rapid Testing: Microfluidic biochemical analyzers provide results in minutes with minimal sample volume.
Portability & Ease of Use: All reagents are pre-stored on-chip, allowing simple, user-friendly operation.
These advantages make microfluidic biochemical analysis ideal for POCT, chronic disease management, and emergency diagnostics. Seamaty's biochemical analyzer uses microfluidic chips to read reagent disks, enabling faster and more accurate detection.
Microfluidics has revolutionized in vitro diagnostics, enhancing molecular diagnosis, immunodiagnosis, and biochemical analysis. By offering automation, rapid processing, high sensitivity, and portability, microfluidic IVD devices are transforming disease detection and healthcare accessibility. As technology advances, microfluidics will continue to shape the future of medical diagnostics, making tests more efficient, affordable, and widely available.

2024-05-09
Demystify fully automatic biochemistry analyzers! This guide explores pricing, top manufacturers (Beckman Coulter, Roche Diagnostics, Siemens Healthcare) and analyzer types (modular, microprocessor-controlled, manual). Learn how these machines revolutionize patient care.

2023-11-06
Discover the essential factors for selecting veterinary blood gas electrolyte analyzers in small animal hospitals. Learn about the game-changing Seamaty VG1, a portable solution for accurate results, rapid decision-making, and seamless integration, optimizing patient care. Make informed choices with our guide to veterinary equipment.
2021-09-03
Dry chemical analysis is simple, portable, fast, environmental friendly and low cost. Compared with the wet chemical analysis method, dry chemical testing instruments and dry reagents are more portable and can be used to carry out medical and health work in communities and rural areas. Therefore, dry chemical analyzer is especially suitable for primary medical institutions and clinics.