release time:2024-02-18 14:34:24
Welcome to the realm of CLIA(Chemiluminescence Immunoassay) analyzers, the unsung heroes of modern medical diagnostics. In this blog post, we'll unravel the significance of CLIA analyzers in the field of medicine, catering to medical professionals, patients, and the curious minds keen on understanding the intricacies of healthcare technology. Our journey will cover the introduction, principles, and types of CLIA analyzers, culminating with a closer look at the Seamaty SMT780.
"CLIA" primarily refers to the Chemiluminescence Immunoassay technique, a highly sensitive and specific method used in various diagnostic tests for detecting biological molecules like hormones, vitamins, drugs, and even infectious diseases. CLIA analyzers, therefore, are sophisticated instruments specifically designed to perform these tests. While laboratories utilizing CLIA analyzers typically operate under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (regulations ensuring quality and accuracy of laboratory testing), the two terms are not directly interchangeable.

Think of a glow stick. To break it open and make it glow, you need to snap it. In a CLIA analyzer, something similar happens. Special chemicals in the test mix act like the "snap" in the glow stick. When they encounter the target molecule (the one being tested for), they trigger a chemical reaction. This reaction creates a temporary form of the molecule with extra energy (like the excited state in your explanation). However, unlike the glow stick, this "excited" molecule quickly releases its energy as light. The brighter the light, the more target molecules were present in the sample.
Inside the analyzer, a special detector called a photomultiplier tube (PMT) acts like a light sensor, similar to the camera in your phone. This sensor is very sensitive and can even detect single photons (tiny packets of light). With each pulse of light from the reaction, the PMT sends a signal that gets stronger or weaker depending on the light intensity. This signal is then converted into a number that the computer can understand, allowing it to calculate the amount of the target molecule in your sample.
Not all CLIA analyzers are created equal. They vary in size, automation level, and application. Here's a glimpse into the diverse world of these instruments:
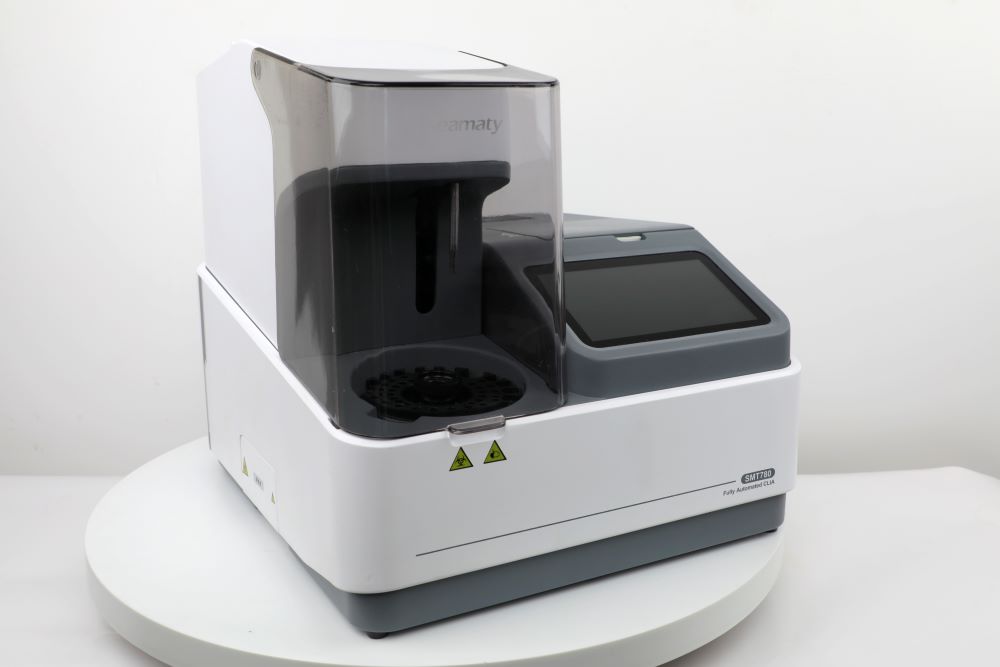
Introducing the Seamaty SMT780
Speaking of POC analyzers, let's take a closer look at the Seamaty SMT780 as a specific example. This compact, automated CLIA analyzer embodies the advantages of its category. Its microcapillary technology and advanced antibody labeling techniques enable fast and accurate testing with minimal sample volume (as little as 10 μL of blood!). Additionally, its user-friendly design and small footprint make it ideal for smaller labs or clinics with limited space. With a capacity of up to 80 tests per hour and 20 test positions, the Seamaty SMT780 offers efficient results without compromising accuracy.
The world of CLIA analyzers is constantly evolving, embracing new technologies and pushing the boundaries of accessibility and affordability. As these advancements unfold, we can expect even faster, more precise, and user-friendly analyzers, potentially expanding their reach beyond traditional laboratory settings and empowering personalized medicine approaches.
This blog post is just a starting point. If you've got specific questions about CLIA analyzers or their applications, feel free to chat with a healthcare pro or dig into resources from organizations like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Understanding these nifty tools helps us appreciate the tech behind better healthcare experiences for everyone. And if you are interested in Seamaty SMT780 CLIA analyzer, feel free to contact Seamaty team to know its specific features, functions and price.
Related further reading:
1. The Pros and Cons of Using Chemiluminescence Immunoassay (CLIA) Analyzers in Your Lab
2. Revolutionize Your Lab Efficiency with the SMT780 Immunoassay Analyzer
3. What is Chemiluminescence Immunoassay | Chemiluminescence Examples

2023-09-12
A dry chemistry analyzer is a machine that is used to analyze the chemical composition of a sample. It uses principles of thermodynamics and diffusion to measure concentrations of various molecules in a sample.
2022-02-23
Blood biochemistry is an important part of clinical biochemistry testing. With the rapid development of science and technology, more and more scientific research results are applied to blood biochemistry tests,
2021-08-04
Although nconventional animals have suddenly broken the traditional pattern of the pet market framed by cats and dogs, the services and help provided by pet hospitals for unconventional animals have not yet kept up with ....