release time:2024-02-05 10:20:55
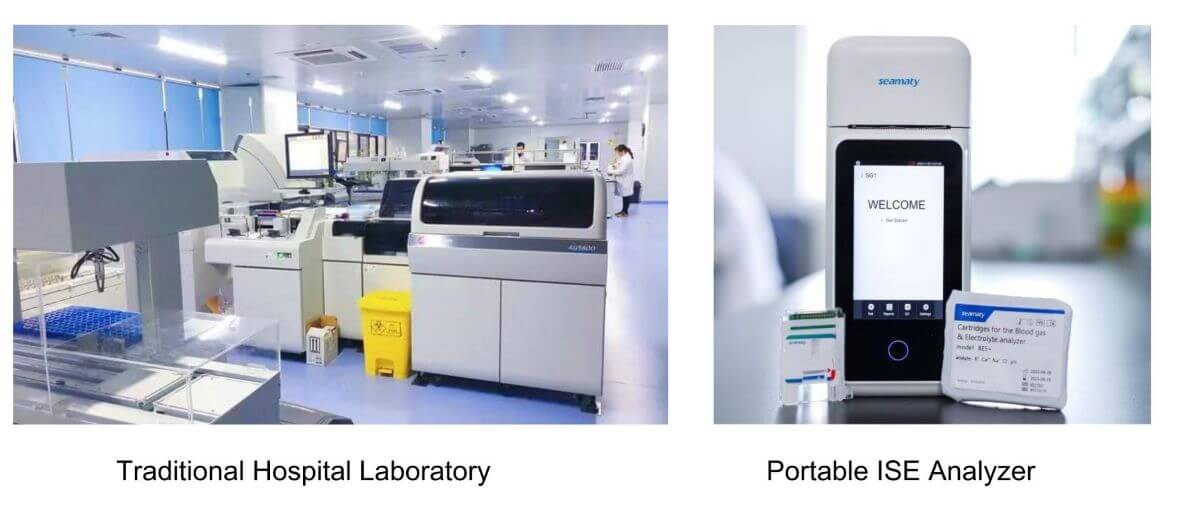
Blood gas analysis stands as a cornerstone in healthcare, offering a window into a patient's respiratory and acid-base balance. Traditionally, this glimpse depended on laboratory tests, often delaying crucial decisions. But enter the portable blood gas analyzer, a compact marvel transforming point-of-care testing.
Ever wondered how these pocket-sized labs work their magic? Get ready to delve into the fascinating working principle of blood gas analyzers. We'll peel back the layers, exploring the intricate dance of electrodes, measurements, and data analysis that unlocks vital health insights in mere minutes. So, buckle up and join us on this journey as we unveil the magic behind these medical powerhouses!
Portable blood gas analyzers are compact devices designed for on-the-go diagnostics, offering a quicker alternative to traditional laboratory-based methods. They boast key features such as portability, speed, and user-friendliness, setting them apart from their more cumbersome counterparts.
Enter the Seamaty SG1, a handheld marvel that embodies these advantages. Weighing in as a portable powerhouse, the SG1 not only provides speedy results within 4 minutes but also stands out with its built-in printer and ease of use, making it an ideal choice for point-of-care diagnostics.
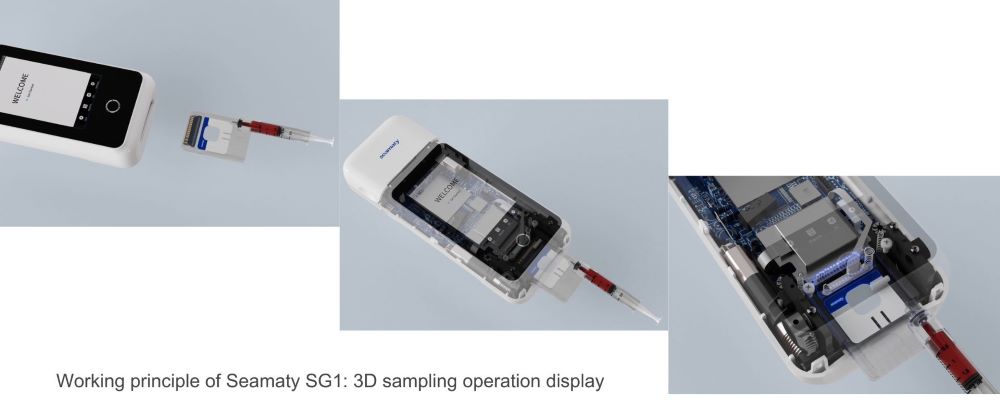

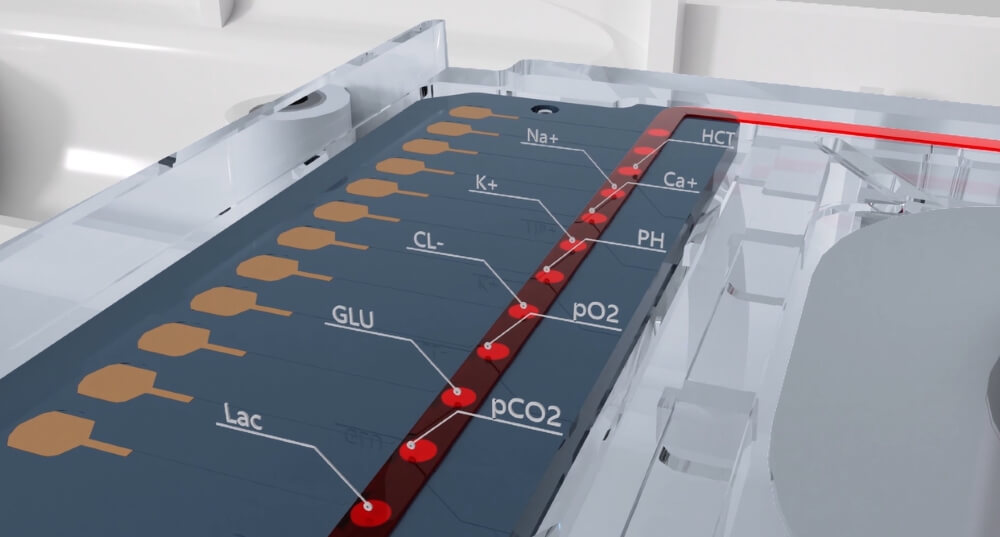
Let's unravel the mystery behind the working principle of portable blood gas analyzers in simple terms. It all starts with the introduction of a small arterial blood sample. Here, the Seamaty SG1 shines by utilizing dry electrode technology, eliminating the need for wet reagents and simplifying the operation.
The electrochemical measurements play a pivotal role. The pH, PO2, and PCO2 electrodes are the unsung heroes, measuring blood acidity, the partial pressure of oxygen, and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide, respectively. The Seamaty SG1, with its advanced technology, ensures accuracy and efficiency in these measurements.
Signal processing and data analysis follow suit, with the Seamaty SG1's microcomputer doing the heavy lifting. The calculated results, including pH, PO2, PCO2, and additional parameters, are then displayed – a seamless process made possible by the user-friendly design of the SG1.
Portable blood gas analyzers bring a slew of advantages to the table. Their speed ensures faster turnaround times, critical for timely decision-making in emergency situations. Improved patient outcomes, especially in critical care scenarios, showcase the real impact of these devices.
The Seamaty SG1, in particular, stands tall in these applications. Imagine a 4-minute window that can make a significant difference. The built-in printer further facilitates quick documentation, enhancing the overall efficiency of the healthcare process. The SG1's ability to measure additional parameters, like electrolytes and metabolites, broadens its diagnostic capabilities.
These portable powerhouses find applications in diverse healthcare settings. In emergency medicine and critical care, where every second counts, the SG1's quick results become a game-changer. In ambulatory care and point-of-care testing, the portability of these analyzers ensures flexibility and convenience.
Additionally, in remote healthcare and resource-limited settings, where access to traditional labs may be challenging, portable blood gas analyzers become invaluable tools.
In this voyage through the inner workings of blood gas analyzers, we've uncovered the essence of point-of-care diagnostics. From the fundamental working principles to the real-world impact, including the exceptional Seamaty SG1, these devices stand as beacons of progress. As we conclude, let's appreciate the strides made in healthcare, where technology not only enhances efficiency but holds the potential to save lives. Embrace the knowledge, explore further, and let's collectively shape a future where swift and accurate diagnostics become the cornerstone of patient care.
Additional further reading:
1. What to Consider When Choosing a Blood Gas Analyzer for Your Healthcare Facility
2. Portable Blood Gas Analyzers: Empowering Remote Healthcare and Emergency Medical Services
3. Decoding Blood Gas Analyzers(BGA): Selecting, Applications, and Top 6 Picks
4. Top 8 Blood Gas and Electrolyte Analyzers in 2024: Brands, Features, Prices
5. Handheld Blood Gas Analyzers Comparison: Abbott i-STAT vs. Siemens EPOC vs. Seamaty SG1
6. A Cost-Effective Alternative to the Abbott i-STAT: Seamaty SG1 Blood Gas&Electrolyte Analyzer
7. Seamaty SG1 Blood Gas Analyzer: A Must-Have for Small Clinics
8.From Novice to Pro: Mastering the Seamaty SG1 Blood Gas Analyzer

2024-12-12
Revolutionize point-of-care testing with portable ISE analyzers! These handheld electrolyte analyzers deliver immediate results, transforming patient care in critical care, chronic disease management, and more. Dive into the possibilities with our blog post and discover the future of medical diagnostics!

2022-08-04
Biochemical analyzers are devices that automate the operation of biochemical analysis processes using physical, chemical, and computer technologies. The automated process of a biochemistry analyzer can include: identification and sample delivery, loading of samples and reagents, charging reaction and detection conditions (e.g., wavelength, temperature, time), data processing, and system maintenance.

2021-10-20
Some of the current POCT biochemistry analyzers have not only solved the problem of speed. The accuracy of the instrument has also been greatly improved. Some biochemistry analyzers can even compete with large instruments.