release time:2024-03-12 13:54:15
Whether in respiratory care, the ICU, or emergency departments, blood gas analysis is an indispensable diagnostic tool. It not only involves respiratory, circulatory, and metabolic functions but also serves as a crucial basis for clinical diagnosis and disease treatment. When choosing a blood gas analyzer, we often hear about "dry" and "wet" types. What exactly sets them apart? Today, let's delve into the discussion.
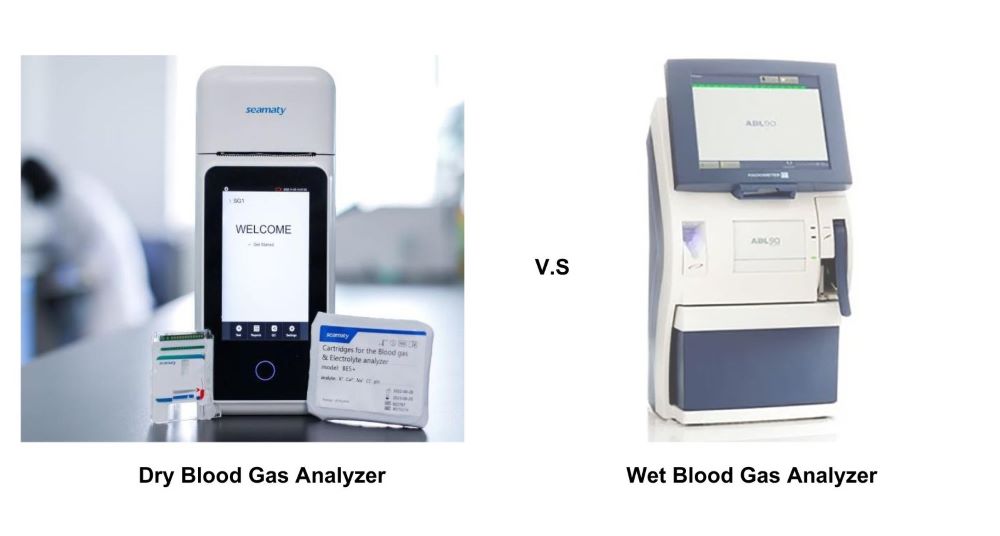
Dry Blood Gas Analyzer:
Wet Blood Gas Analyzer:
In summary, dry and wet blood gas analyzers each have their advantages and disadvantages, catering to different scenarios and applications. In practical use, the choice of the instrument should depend on specific circumstances.
The Seamaty SG1 Blood Gas Electrolyte Analyzer employs dry electrochemical technology combined with microfluidic techniques, providing accurate results comparable to industry-standard desktop machines. The compact and convenient design makes it suitable for bedside testing in related departments without spatial constraints. The instrument has no internal fluid pathways, requires no maintenance, and offers easy and fast operation. The sample testing time is only 50 seconds (four minutes including sample preparation and report printing), achieving real-time testing and meeting the diverse needs of various clinical departments.
2022-02-23
Blood biochemistry is an important part of clinical biochemistry testing. With the rapid development of science and technology, more and more scientific research results are applied to blood biochemistry tests,

2021-12-27
Because their treatment is fairly simple and relatively straightforward. But many pet owners don't know this. If left untreated and allowed to develop, these infections can cause health problems. If they do not increase in mobility or weight, they can lead to a risk of zoonosis.

2021-08-03
Seamaty SMT-120VP pet automatic biochemical analyzer, a multifunctional instrument, can detect routine biochemistry, coagulation (4 items), blood gas electrolytes (including pH), and some immune items (c-CRP, f-SAA).