release time:2024-08-01 15:13:17
Blood tests are essential tools used by healthcare providers to assess overall health, diagnose diseases, and monitor treatment effectiveness. While the results can be confusing, understanding the basics of common blood tests can empower you to take an active role in your healthcare. This guide will provide a simple explanation of common blood tests and how to interpret your results.
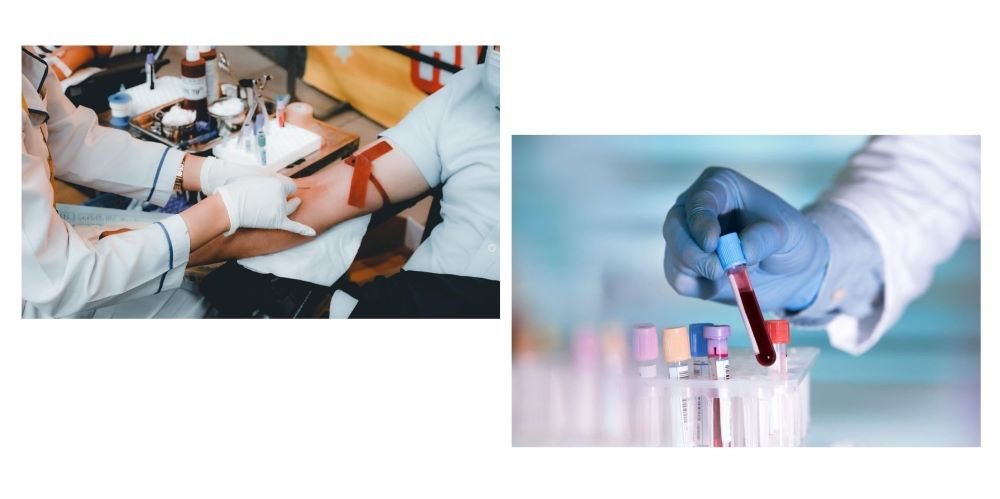
While blood test results often include reference ranges, interpreting these numbers can be complex. It's essential to consult with your healthcare provider for a comprehensive understanding of your specific results. However, this section provides a basic overview of common blood test parameters:
A blood routine test, often referred to as a Complete Blood Count (CBC), provides a comprehensive overview of your blood health. It includes:
A blood lipid test, also known as a lipid panel, assesses your heart health by measuring various fats in your blood:
Measures blood sugar levels. High levels can indicate diabetes.
Understanding your blood test results is a crucial step in managing your health, but interpreting these results can be complex. While your healthcare provider is the ultimate authority on your specific situation, having access to advanced blood testing tools can significantly enhance the diagnostic process.
Seamaty offers innovative solutions designed to streamline blood testing and provide accurate results efficiently. Seamaty SD1 biochemical analyzer is ideal for small clinics and family practices, offering a comprehensive range of tests. For immediate and on-site results, the Seamaty SG1 blood gas analyzer is a valuable tool for emergency situations.
Seamaty SD1 Biochemical Analyzer: Delivers precise results for a variety of biochemical tests, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various health conditions.
Seamaty SG1 Blood Gas Analyzer: Provides rapid analysis of blood gases, electrolytes, and critical care parameters, enabling timely decision-making in critical situations.

To illustrate the comprehensive capabilities of our analyzers, here are sample reports demonstrating the diverse range of tests that can be performed:
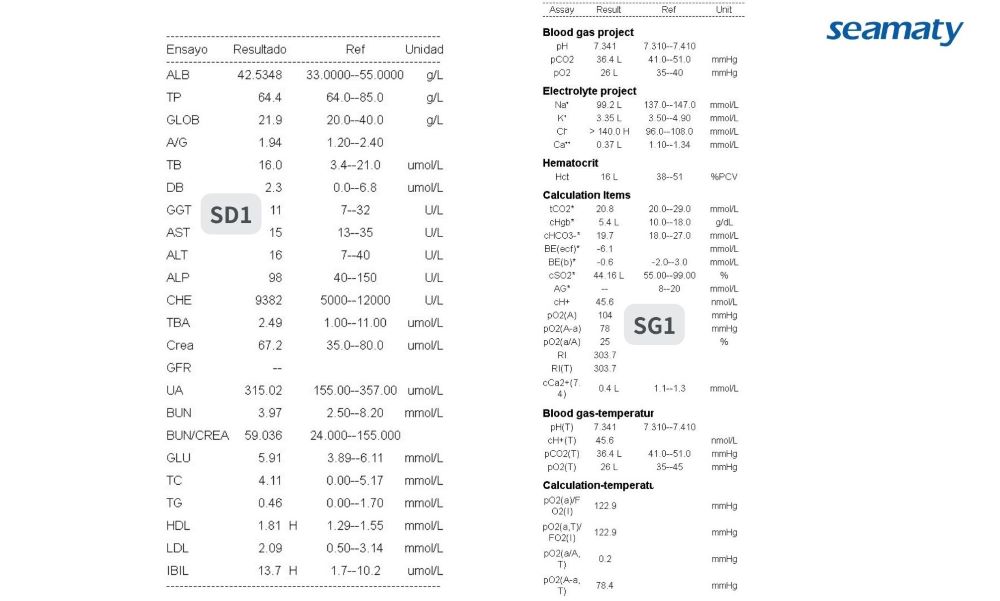
By incorporating these advanced tools into your practice, you can improve patient care, increase efficiency, and enhance diagnostic accuracy.
Understanding your blood test results is an important step in managing your health. By familiarizing yourself with common blood tests and their implications, you can better communicate with your healthcare provider and make informed decisions about your well-being. Remember, this guide is intended for general knowledge and should not replace professional medical advice

2022-06-22
These blood analyzers are very useful in providing quick and accurate information about the blood cell count and its properties. The most common information obtained with the help f these analyzers are
2022-05-11
After the blood leaves the body in the natural environment, non-anticoagulated specimens will quickly coagulate and precipitate is serum. Some specimens are used a variety of anticoagulants,
2022-02-17
In addition to DR and ultrasound, CT can also help veterinarians determine a pet's condition. What is CT? How does it work? What does it do? Read on.