release time:2021-11-08 16:41:25
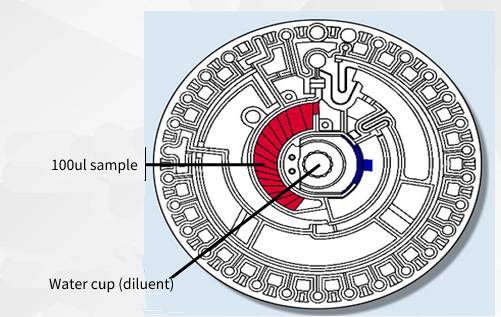
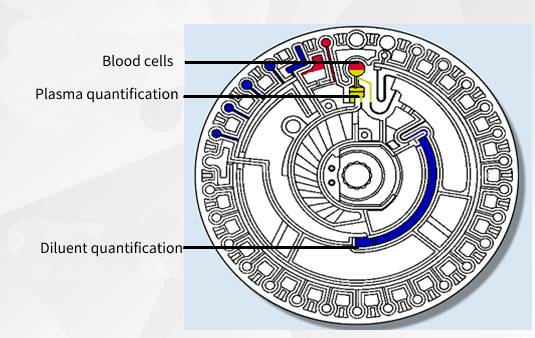
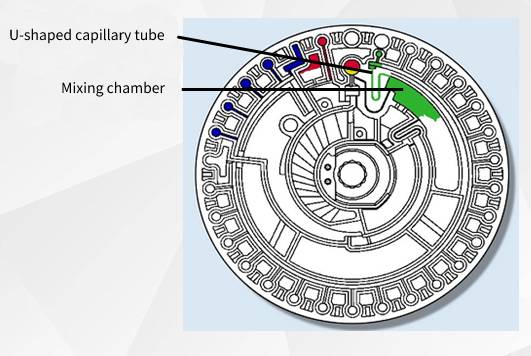
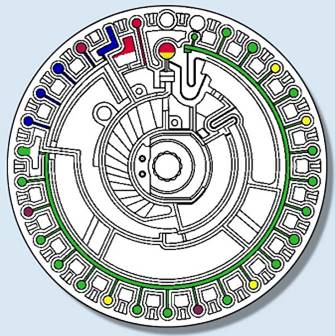
The built-in motor of the biochemical instrument drives the test disc at high speed. Under centrifugal force, the sample and diluent move towards the outer periphery away from the center of the test disc (built-in centrifugation). After a period of high-speed operation, the sample is separated into plasma against the center of the circle, a fixed volume, and blood cells against the periphery by a small centrifugal force (sample centrifugation for quantitative stratification). On the other hand, a certain volume of diluent is retained in the circular cavity. The rest enters the quality control chamber for comparable color assays and the excess diluent collection chamber.

2023-04-17
The article discusses common errors and pitfalls in clinical chemistry analyzer testing, and the keywords related to this topic include clinical chemistry analyzer, testing errors, laboratory testing, sample collection, instrument malfunctions, calibration errors, reagent storage, quality control, hemolysis, and contamination.
2022-03-16
The blood taken for biochemistry cannot be used for routine blood tests, coagulation, tumour indicators, hepatitis B or HIV. For these items, a separate blood draw is required

2021-09-01
Point-of-care testing (POCT) refers to clinical testing performed next to the patient (bedside testing.) POCT is usually not necessarily performed by a clinical laboratory technician, but is analyzed immediately at the sample site. This test method eliminates the complex processing of samples during laboratory testing, resulting in rapid test results.