release time:2023-08-04 14:50:28
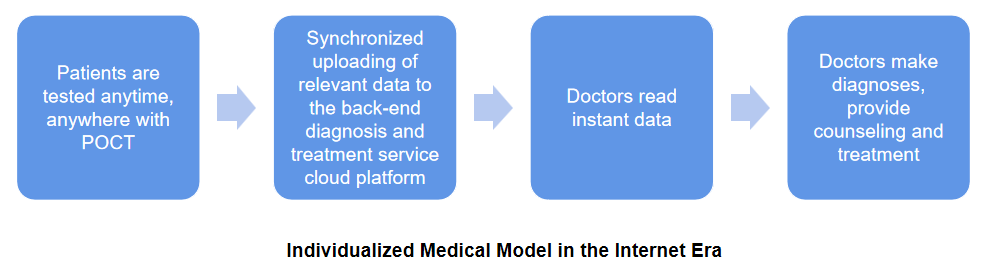
POCT, short for Point of Care Testing, refers to rapid and convenient testing conducted at the patient's side, reducing the need for sample transportation and shortening reporting times. POCT is a rapidly growing segment in the field of in-vitro diagnostics. Compared to traditional department or laboratory diagnostics, POCT retains the core steps of "sampling, analysis, quality control, output," significantly reducing diagnosis time. It also offers greater flexibility in testing space and allows non-specialist operators, even the patients themselves, to perform the tests.
The dry chemistry technique is an alternative to traditional wet chemistry. It involves using the liquid in the test sample as a reaction medium, where the analyte directly reacts with dry reagents immobilized on a carrier. The analysis can be qualitative by visual observation or semi-quantitative using instruments. This method is suitable for testing samples such as whole blood, serum, plasma, and urine.
Chemiluminescent immunoassay combines highly sensitive chemiluminescent detection technology with highly specific immune reactions for detecting various antigens, semiantigens, antibodies, hormones, enzymes, fatty acids, vitamins, and drugs. Common chemiluminescent markers include acridinium esters. This method can be used to detect and identify unknown antigens, myocardial markers, tumor markers, hormones, and various proteins.
Immunochromatographic technique involves fixing specific antibodies onto nitrocellulose membranes in certain zones. When a dried nitrocellulose end is immersed in the sample, the sample migrates along the membrane by capillary action. When it reaches the area with fixed antigens, the corresponding antigens in the sample bind specifically to the antibodies. Using immunogold colloids or immunoenzymes, this area shows a specific color, allowing for specific immune diagnostics. This method can be used to detect myocardial markers, hormones, and various proteins.
Biosensors utilize the molecular recognition function between active substances such as proteins, enzymes, and nucleic acids to convert the microscopic changes in the target substance's conformation or concentration into quantifiable or visual signals such as electric signals or fluorescence. They consist of biochemical recognition elements and signal transducers. They can detect proteins, nucleic acids, drugs, challenging-to-culture bacteria, viruses like chlamydia, tuberculosis, human immunodeficiency virus, etc.
Microfluidics technology involves manipulating fluids in micro-nano-scale spaces. It integrates the basic operational units of sample preparation, reaction, separation, and detection in medical analysis onto a small chip, automatically completing the entire analysis process with precise control over sample and reagent quantities and flow rates. It allows the flexible combination and scale integration of various unit technologies on a controllable micro-platform. Common implementations include pneumatic-driven and centrifugation-driven methods. When combined with biosensors, this technology can be used to detect nucleic acids, proteins, and other biological molecules and cells.
POCT products can be used in various settings, including clinical departments, outpatient clinics, emergency rooms, ICUs, operating rooms, monitoring rooms, primary hospitals, community health centers, private hospitals, medical examination centers, wellness centers, health service centers, disease control centers, disaster medical rescue sites, food safety monitoring sites, environmental protection sites, customs quarantine, illicit drug screening, forensic scenes, biological anti-terrorism scenes, etc.
Common testing areas for POCT include blood glucose, cardiovascular diseases, coagulation/thrombolysis, infection factors, blood gas/electrolyte, pregnancy, tumor markers, renal markers, drugs (abuse), alcohol, and other subcategories.
In conclusion, POCT is rapidly advancing in the field of medical diagnosis and plays an increasingly significant role in diagnostics, chronic disease management, basic public health services, therapeutic monitoring, and more.
Application Scenario
Application Field
Primary Purpose
Hospital
Emergency Lab
Provide timely testing information for rescuing patients
Hospital Intensive Care Units(ICU)
Connected to physiological monitors to provide real-time laboratory data
Subspecialty clinics
CRP testing, myocardial infarction and heart failure testing, blood glucose testing, pregnancy testing, etc
Hospital clinical lab
Detection of infectious diseases, influenza, etc
Small Medical Institutions
Health centers, community clinics, physician clinics, etc
Urinalysis, dry biochemical detection, hepatitis detection, etc
Domestic Use
Personal use
Various types of monitoring such as blood pressure and blood sugar
First Aid Scene
Ambulance
Detection of myocardial markers and electrolytes
Diagnostic Applications
Pediatric diseases
CRP testing, inflammation testing, etc
Cardiovascular diseases
Heart failure and myocardial infarction detection
Blood related diseases
Thrombosis and hemostasis, hemoglobin quantification and blood cell count, hemorheological analysis, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and other tests
Infectious diseases
Rapid qualitative detection of antigens and antibodies against hepatitis B B virus, syphilis, HIV, etc
Endocrine diseases
Detection of blood glucose, Glycated hemoglobin and microalbuminuria
Fever related diseases
Combined blood routine and CRP testing, etc
Blood biochemical analysis
Dry chemistry, electrolyte and blood gas analysis, Hs-CRP (quantitative gold labeling method for detecting highly sensitive CRP), cholesterol chip, etc
Pregnancies
pregnancy checkup
TORCH-IgM Five Quick Detection Card
Other Scenarios
Supervision and law enforcement, etc
Prohibition of drugs, drunk driving, food testing, etc
As a leading company in the Chinese POCT industry, Chengdu Seamaty Technology Co., Ltd., not only holds the German TÜV Rheinland ISO 13485:2016 quality management system certification but also obtained CFDA medical device product registration certificates and medical device CE certification. After years of development, the company has not only built a microfluidic biochemical technology platform and a blood gas&electrolyte platform but has also independently developed the world's first capillary chemiluminescence detection platform. Relying on these platforms, the company has formed a rich product line in fields such as liver diseases, kidney diseases, diabetes, pancreas, cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular diseases, kidney diseases, inflammation, tumor markers, thyroid diseases, and infectious diseases. These products find extensive applications in primary medical care, emergency rescue, oral aesthetics, and veterinary in-vitro diagnostics, among other scenarios.

2023-09-04
Discover why small clinics require a portable blood analysis machine and gain insights on selecting the ideal one for your healthcare facility. Explore the importance of portable blood analysis machine for small clinics in this informative guide.

2023-06-30
Discover how to test hypothyroidism in dogs using cTT4 analysis on the VG2 Vet Analyzer. Learn about its features, benefits, and follow the step-by-step guide for accurate diagnosis and treatment.

2022-03-14
Currently, there are two main types of COVID-19 virus detection methods: one is based on nucleic acid detection at the molecular level; the other is based on immunological principles, mainly antigen detection and antibody detection.