release time:2023-10-16 14:56:43
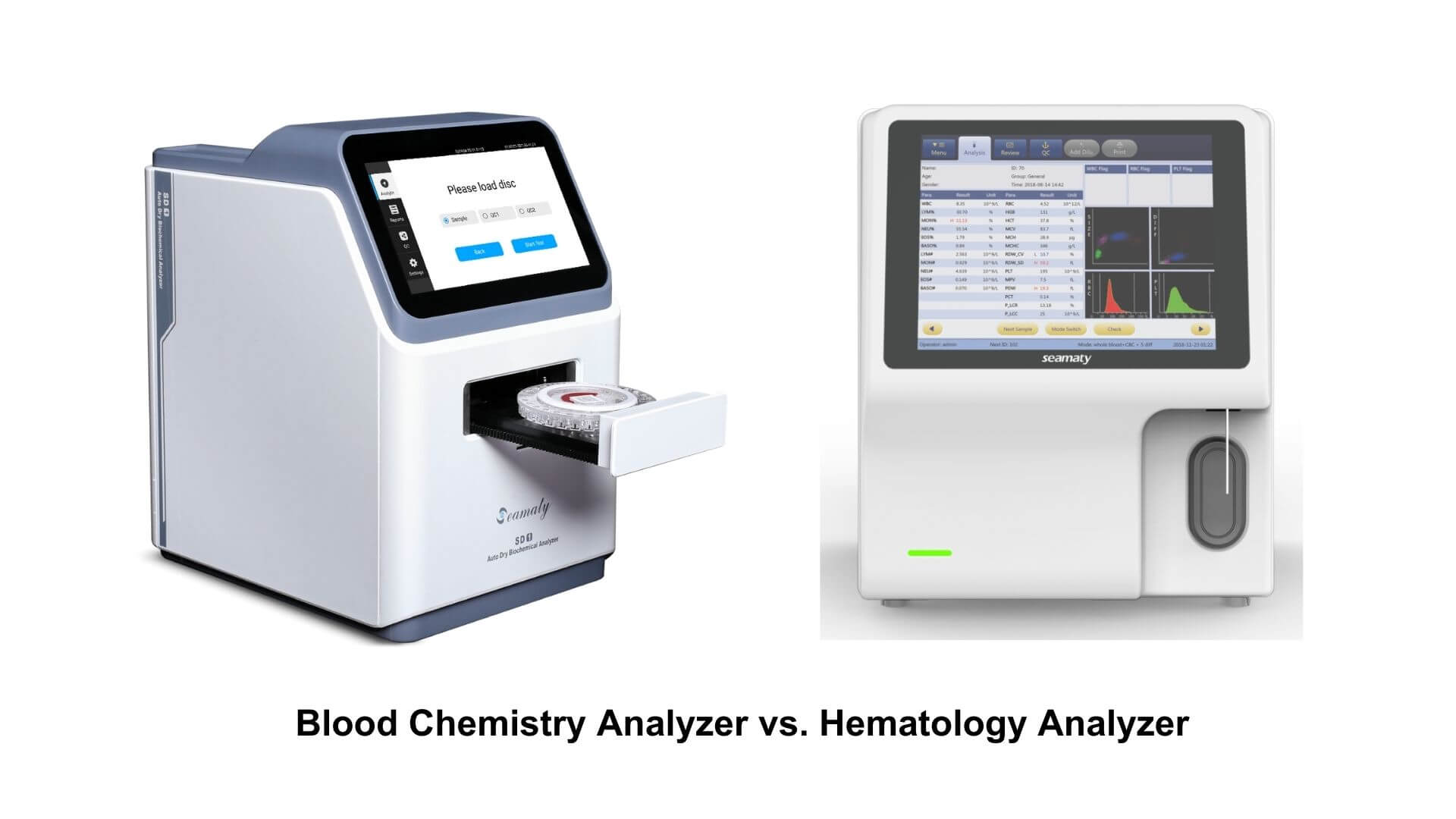
Blood analysis is a fundamental aspect of modern healthcare, providing vital insights into a person's health and aiding in the diagnosis and management of various medical conditions. Two critical tools in blood analysis are the blood chemistry analyzer and the hematology analyzer. In this article, we will explore these analyzers, highlighting their key differences and illustrating their significance through specific examples—the Seamaty SD1 blood chemistry analyzer and the Seamaty 5-part auto hematology analyzer.
A blood chemistry analyzer, also known as a clinical chemistry analyzer, analyzes the chemical and biochemical components of blood, including glucose, cholesterol, electrolytes, enzymes, hormones, and other substances. It provides information about organ function and metabolic status, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of various medical conditions like diabetes, liver disease, kidney disease, and cardiac disorders.
Blood chemistry analyzers typically analyze anti-coagulation whole blood, serum, and plasma samples.
Parameters analyzed by blood chemistry analyzers include glucose levels, lipid profiles, liver and kidney function markers, electrolyte levels, and various other biochemical components essential for understanding a person's metabolic status.
Blood chemistry analyzers use advanced technologies to measure and quantify the chemical components in a blood sample. These may include enzymatic assays, spectrophotometry, immunoassays, and ion-selective electrode (ISE) methods.
The Seamaty SD1 blood chemistry analyzer is an automated device designed for on-site testing, enabling quick and accurate medical diagnosis. With a built-in centrifuge, real-time quality control, and QR code integration, it provides efficient analysis of small blood samples and delivers results within 12 minutes.
Blood chemistry analyzers are utilized in a wide range of medical settings, from hospitals and laboratories to clinics and point-of-care facilities. They play a crucial role in diagnosing conditions such as diabetes, liver and kidney disorders, cardiac diseases, and more.
A hematology analyzer is a medical device designed to analyze blood for the cellular components, primarily focusing on the formed elements of the blood, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It provides information on cell counts, cell size, cell morphology, and other related parameters. Hematology analyzers are crucial for diagnosing conditions like anemia, infections, and blood clotting disorders.
Hematology analyzers typically analyze whole blood and pre-diluted blood samples.
Parameters analyzed by hematology analyzers include red blood cell count, white blood cell count, hemoglobin levels, hematocrit, platelet count, and various indices related to blood cell size and shape.
Hematology analyzers use technologies such as laser scattering, impedance, and flow cytometry to analyze blood cells and provide accurate and detailed information about their characteristics and proportions.
The Seamaty 5-part auto hematology analyzer utilizes laser scattering technology for precise analysis of blood cell components. With a compact design and integrated reagent cabinet, it offers reliable results and an excellent user experience.
Hematology analyzers are critical in diagnosing and monitoring various blood disorders, including anemia, infections, clotting disorders, and leukemia. They are extensively used in hospitals, laboratories, and clinical settings.
Blood chemistry analyzers focus on chemical and biochemical components, while hematology analyzers analyze cellular components of blood.
Blood chemistry analyzers analyze anti-coagulation whole blood, serum, and plasma, whereas hematology analyzers analyze whole blood and pre-diluted blood.
Blood chemistry analyzers use enzymatic assays, spectrophotometry, immunoassays, and ISE methods, while hematology analyzers utilize laser scattering, impedance, and flow cytometry.
Blood chemistry analyzers aid in diagnosing metabolic disorders and organ function assessment, while hematology analyzers are essential for diagnosing blood disorders and conditions affecting blood cell components.
|
Aspect |
Blood Chemistry Analyzer |
Hematology Analyzer |
|
Analyzed Components |
Chemical and biochemical components (e.g., glucose, cholesterol) |
Cellular components (e.g., red blood cells, white blood cells) |
|
Sample Types Analyzed |
Anti-coagulation whole blood, serum, plasma |
Whole blood, pre-diluted blood |
|
Technology Utilized |
Enzymatic assays, spectrophotometry, immunoassays, ion-selective electrode methods |
Laser scattering, impedance, flow cytometry |
|
Applications and Medical Relevance |
Metabolic disorder diagnosis, organ function assessment |
Blood disorder diagnosis, assessment of blood cell characteristics |
Understanding the differences between blood chemistry analyzers and hematology analyzers is crucial for appreciating their distinct roles in the realm of medical diagnostics. While blood chemistry analyzers focus on analyzing biochemical components, hematology analyzers delve into the cellular aspects of blood. Both types of analyzers are indispensable, complementing each other to provide a comprehensive understanding of a patient's health and facilitating timely and accurate medical interventions. The Seamaty SD1 blood chemistry analyzer and the Seamaty 5-part auto hematology analyzer serve as excellent examples, showcasing the advancements in technology and their significant contributions to modern healthcare.

2024-02-18
Explore the intricacies of CLIA Analyzers in this comprehensive guide. Uncover their significance in medicine, understand the working principles with simplified explanations, and discover various types, including the advanced Seamaty SMT780.
2022-03-09
Biochemical testing requires the collection of patient's blood, but the quality control before biochemical testing is an important link

2022-02-18
1. AST/ALT: Clinical significance of AST/ALT ratio. The AST/ALT ratio is different in patients with different types of hepatitis, for example