release time:2022-10-10 10:20:58
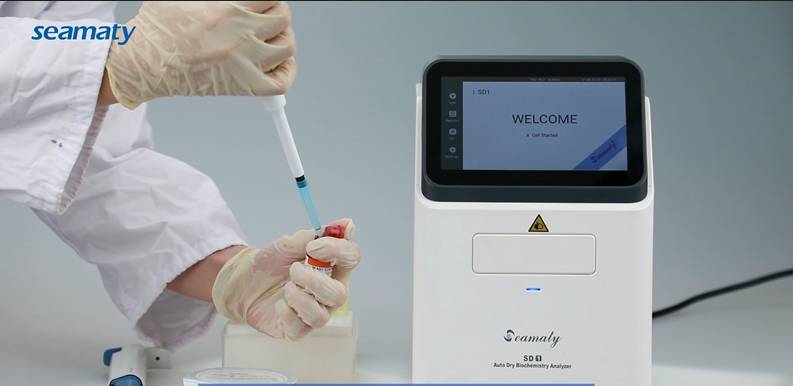
The types of in vitro diagnostic reagents are biochemical diagnostic reagents, immune diagnostic reagents, molecular diagnostic reagents, microbial diagnostic reagents, urine diagnostic reagents, coagulation type diagnostic reagents, hematology and flow, cellular diagnostic reagents.
2023-08-23
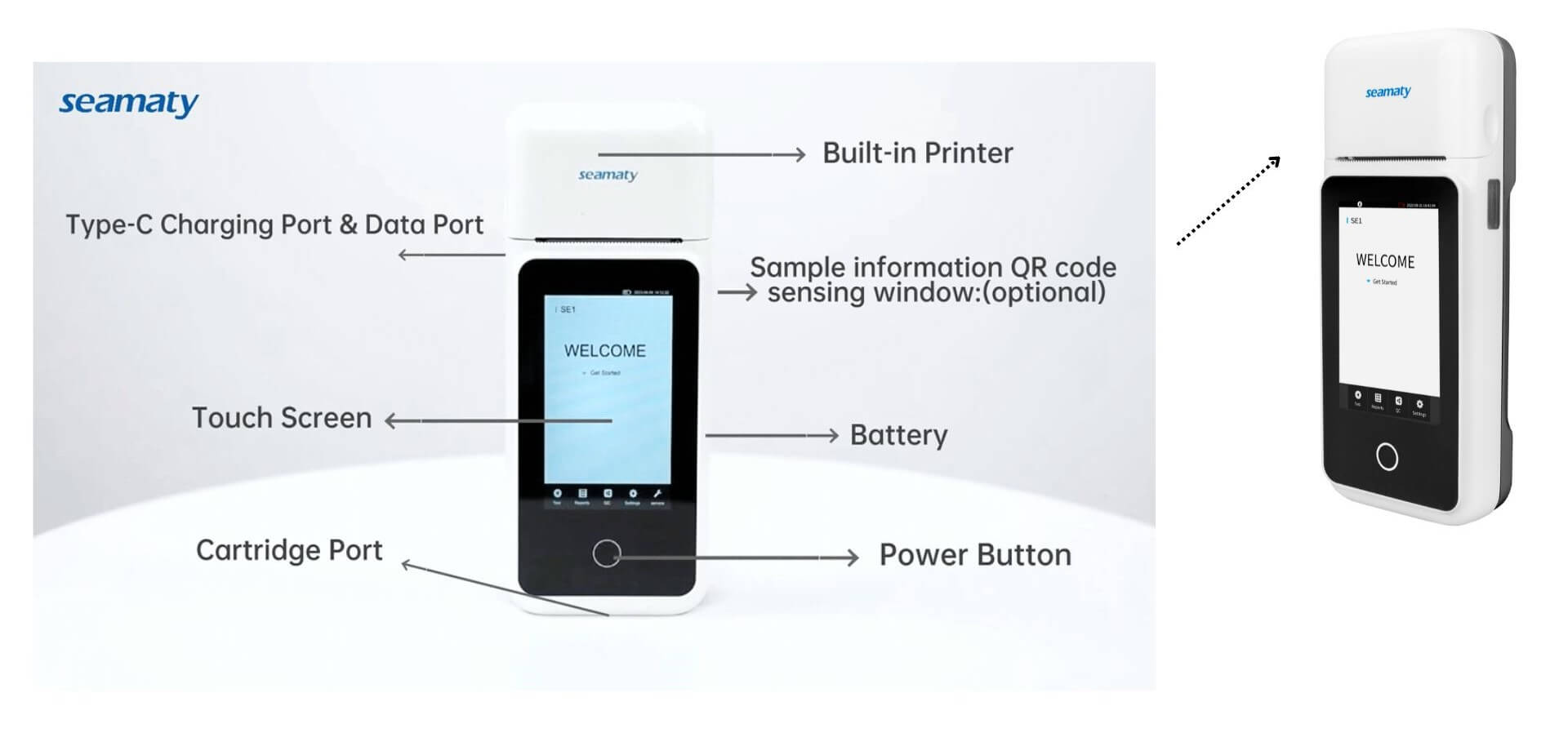
Discover how to pick the perfect electrolyte analyzer for small to mid-sized clinics. Learn about different types, benefits, and Seamaty's SE1 electrolyte analyzer, enhancing patient care with its portable precision.
2023-06-26
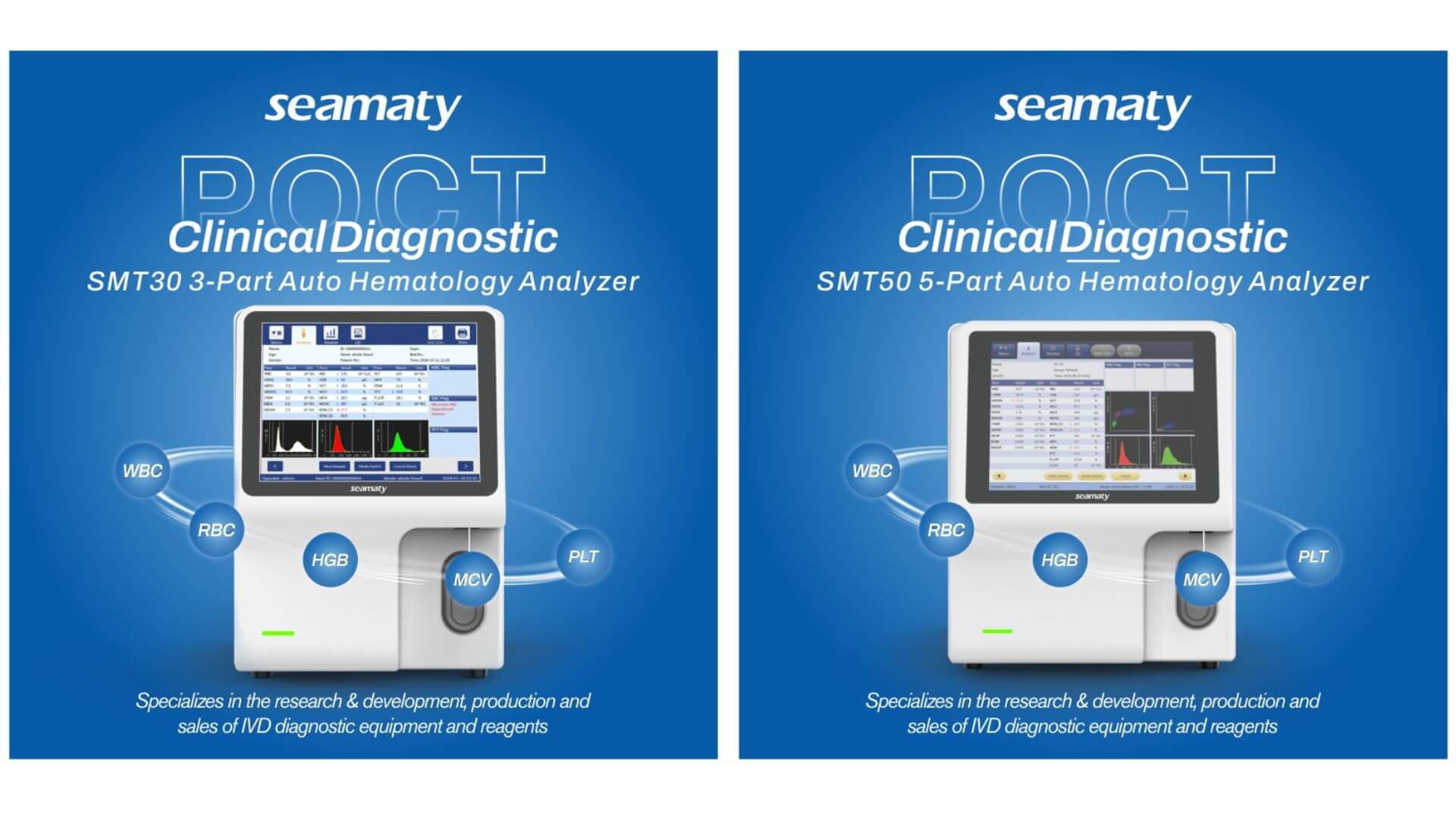
Explore the significance of automated CBC machines in healthcare, their diagnostic capabilities, and Seamaty's advanced SMT-30 and SMT-50 analyzers. Streamline blood analysis, improve diagnostics, and enhance patient care.

2022-04-21
According to the type of chemical reaction, chemistry analyzers can be roughly divided into dry chemistry analyzers and wet chemistry analyzers. Wet chemistry analyzers are the large, fully automated chemistry analyzers that we commonly see in hospitals.