release time:2024-05-14 14:07:37
Blood gas analysis is a vital tool in a doctor's arsenal, offering a window into a patient's internal environment. By measuring key parameters in arterial blood, it helps diagnose and manage critical conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations, and respiratory failure.
This blog post dives into the fascinating world of blood gas analyzers. We'll explore how these machines work their magic, unveil their internal structure, and explain how they play a crucial role in saving lives.

Imagine blood gas analysis as a detailed report on the health of your blood. A blood gas analyzer measures three key parameters:
Think of partial pressure as the amount of pressure exerted by a specific gas in a mixture of gases. In the case of blood, pCO2 and pO2 tell us how much carbon dioxide and oxygen are dissolved in the blood, respectively.
The blood gas analyzer works like a miniaturized laboratory, performing a complex analysis in mere seconds. Here's a breakdown of the magic behind the scenes:
Sample Introduction: Blood is drawn from an artery and introduced into the analyzer using a negative pressure suction system.
Electrode Contact and Reaction: The blood sample comes into contact with specialized electrodes:
Signal Conversion: Each electrode converts the measured parameter (pH, pCO2, or pO2) into a corresponding electrical signal.
Processing and Display: The electrical signals are amplified, converted into a digital format, and sent to the analyzer's microcomputer. The microcomputer processes the data, calculates the final results, and displays them on a screen or prints them out.
The blood gas analyzer is a marvel of engineering, consisting of three key components:
Blood gas analyzers are life-saving tools that provide crucial information for diagnosing and managing a wide range of medical conditions. While requiring arterial blood for analysis (unlike some other blood tests), these machines offer a wealth of information that helps doctors make informed decisions and save lives.
2023-12-12
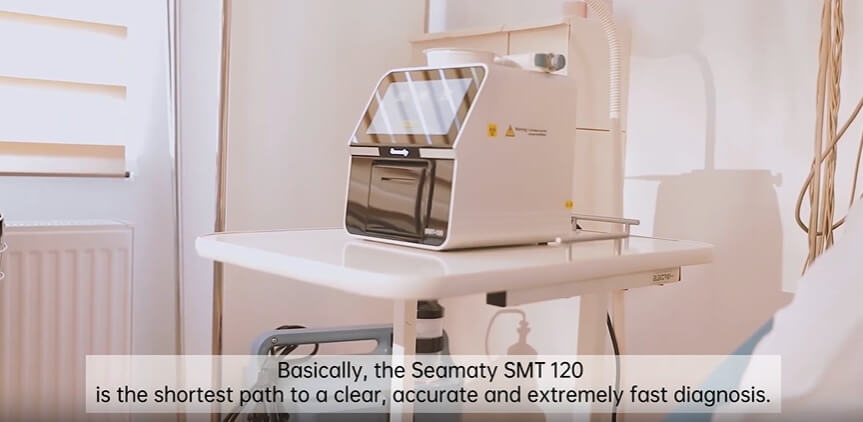
Get reliable results in just 12 minutes with the groundbreaking Seamaty SMT-120 POC chemistry analyzer. This user-friendly device boasts unmatched speed and accuracy for critical decisions, comprehensive testing capabilities, and a cost-effective design that minimizes maintenance. Discover how the SMT-120 is transforming healthcare worldwide!

2022-01-14
The evaluation of IVD analytical performance should be carried out in accordance with the corresponding evaluation plan, and the instruments, reagents, calibrators, testing procedures, etc.

2021-09-06
With the use of various Point Of Care Testing technologies and testing instruments, POCT can be performed both in and out of the hospital. Some special tests can even be performed at home or in special settings (e.g. outdoors, on site), greatly facilitating the needs of patients and special populations. Here are 8 Examples of Point Of Care Testing.