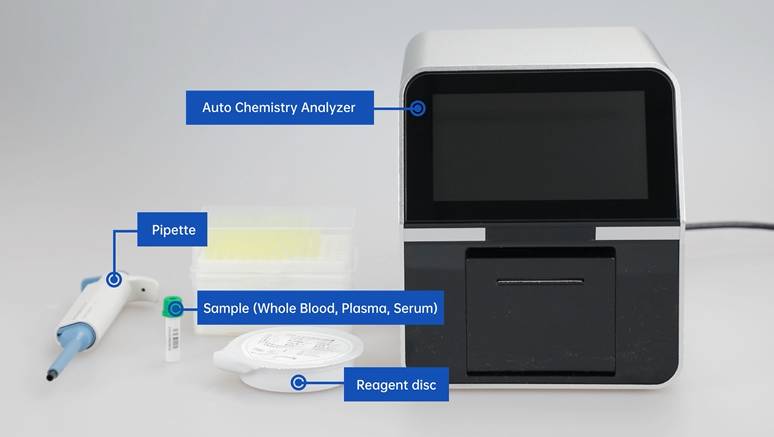
In the previous article, we shared the production process of biochemical reagents. Today, let's understand the main production process of chemiluminescent reagents (taking chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay with microplate carrier as an example).
A. Preparation of solid-phase carriers
1. Preparation of coated plate
Prepare the tested coated plates, record the batch number, number and status identification. Routine quality control items: size, appearance, packaging. 2.
2. Preparation of coating solution
Prepare the coating buffer. Add the wrapped antibody or antigen to the working concentration and mix well to form the required wrapping solution. The working concentration of the coating solution should be used within the specified time. Routine quality control items: formulation of coating buffer, pH value.
3. Coating of coating plate
The coating solution is added to the plate according to the process requirements. Record the number of coated plates. Routine QC items: volume, temperature, time, process monitoring. Key equipment: coating machine, balance, spiker.
4、Preparation of plate washing solution
Prepare plate washing solution according to the recipe (according to the process requirements of each unit, can not wash the plate). Routine quality control items: plate washing solution formulation, pH value.
5、Closing solution preparation
Preparation of closure solution according to the formula. Routine quality control items: formulation of closure solution, pH value.
6. Plate washing and sealing
After the completion of coating, draw off the coating solution from the wells. After washing the plate with the plate washing solution (according to the process requirements of each unit, you can not wash the plate), add the closure solution. Routine quality control items: Closure volume, temperature, time, process monitoring. Key equipment: coating machine, plate washer, balance, spiker.
7. Drainage
After closing the reaction plate, drain the liquid in the wells. Routine quality control items: process monitoring.
8. Drying
The reaction plate should be dried according to the requirements of the process. General quality control items: temperature, humidity, time, process monitoring, etc.
9. Sealed packaging
The dried reaction plate should be sealed and packed in aluminum foil bag. Put desiccant inside (according to the process requirements of each unit, it can be not put). General quality control items: sealing performance, marking and expiration date, etc. Key equipment: packing machine.
10. Reaction plate (semi-finished products) inspection
Sampling and inspection of the reaction plate after bagging and sealing. Routine quality control items: appearance, intra-plate variation, inter-plate variation, etc.
B Titration process
1. Preparation of enzyme conjugate (also called enzyme marker) (according to the actual situation of each product, this step may not be carried out) The relevant antibody (or antigen) is labeled with horseradish peroxidase (or other enzymes) by the conventional sodium periodate-ethylene glycol method. Routine quality control items: labeling method, process control.
2. Identification of enzyme conjugates
-
(1) Functional test The enzyme conjugate will be diluted with enzyme diluent and used for product titration, and the result should meet the quality standard of relevant kits.
-
(2) Stability The enzyme conjugate will be diluted with enzyme diluent and used for 2~8℃ and thermal stability test, and the result of titration should be in accordance with the quality standard of relevant kits.
-
(3) Enzyme conjugate diluent is prepared according to the formula of enzyme conjugate diluent, stored at 2~8℃ and used within the specified time. Routine quality control items: enzyme conjugate diluent formula, pH value.
4. Titration of working concentration of enzyme conjugate Take enzyme conjugate, dilute it to different concentrations with enzyme conjugate diluent, and titrate it with prepared reaction plates. Measure the series of standards and corresponding quality control products to determine the optimal working concentration of the enzyme conjugate.
5. Preparation of enzyme conjugate working solution Mix the required amount of enzyme conjugate and enzyme conjugate diluent according to the titration concentration. Routine quality control items: test before dispensing, test with the matching reaction plate, appearance, sensitivity, quality control determination value, quantitative products should be made for calibration product linearity test.
6. Dispense of enzyme conjugate working solution Dispense enzyme conjugate working solution according to the process requirements. Routine quality control items: confirm the reagent name, batch number, quantity, volume, sealing after packaging before dispensing.
7. Enzyme conjugate working solution (semi-finished product) inspection The enzyme conjugate working solution is sampled and inspected for appearance, dispensing volume, sensitivity, linearity of dose-response curve of calibrator, and determination value of quality control product.
C Preparation of calibrator, negative/positive control or quality control
1. Diluent
Prepare the diluent according to the formula and store it at 2-8℃ or -20℃ or below. And use within the validity period. Routine quality control items: diluent formula, pH value.
2. Preparation of calibrator and negative/positive control
The preparation of calibrators and negative/positive controls should be quantitatively traceable. Refer to the national standards, WHO standards or other levels of standard substances for preparation. Routine quality control items: pre-dispensing test, accuracy, dose-response curve linearity (quantitative products), quality control determination value.
3. Dispensing of calibrators, negative/positive controls or quality control products
The calibrators, negative/positive controls or quality control products are dispensed according to the process requirements. Routine quality control items: confirm the name, batch number, quantity and quantity of reagents before dispensing.
4. Calibration, negative/positive control or quality control product (semi-finished product) inspection
Sampling and testing of calibration products, negative/positive controls or quality control products after packaging, appearance, packaging volume, accuracy, dose-response curve linearity (quantitative products), quality control products measured value.
D Preparation of chemiluminescent substrates
1. Substrate buffer
Prepared according to the formula of the substrate buffer, stored at 2 ~ 8 ℃, and used within the validity period. Routine quality control items: substrate buffer formulation, pH.
2. Preparation of chemiluminescent substrate (oxidant and luminol)
Add the corresponding oxidant and luminol to the substrate buffer according to the formula of oxidant and luminol, respectively. Routine quality control items: oxidant and luminol formulations. Routine QC items: pre-dispensing test, background, luminescence intensity.
3. Substrate chemiluminescence (oxidizing agent and luminol) packaging
According to the process requirements of the sub-assembly of chemiluminescent substrates (oxidants and luminol). Routine quality control items: confirm the name, batch number, quantity of reagents before dispensing, dispensing volume, sealing after encapsulation.
4. Chemiluminescent substrate (semi-finished products) inspection
Sampling and inspection of the chemiluminescent substrate after packaging, appearance, packaging volume, background, sensitivity, luminous intensity.
E Sub-assembly, visual inspection and labeling
The amount of the dispensing is measured by weight loss weighing method, and the mass is converted into volume for the control of the dispensing amount. Visual inspection is to visually check the color of the components, the amount of packaging and whether turbidity, impurities, etc..
F. Packaging
According to the requirements of SOP of reagent kit packaging and instructions, packaging is carried out in the form of assembly line operation. When packing, we should strictly check the name, batch number and loading quantity, carefully check the quantity of each material, and double check before closing the box.